To improve the landscape design and ease of use of a site with differences in elevation, a concrete retaining wall (RC) of several types is used. The structure is necessary for terracing, zoning, eliminating erosion and strengthening slopes. Retaining walls can protect columnar grillages, slab and strip foundations from the effects of lateral movements of heaving soils.
When making calculations, you must follow the instructions of SP 43.13330.2012 (clause 5.1).
Construction of a retaining wall
When all the parameters have been calculated and the configuration and dimensions of the wall have been selected, you can begin its construction
Trench
This is the first stage of construction of the supporting structure. Markings are applied to the land plot in accordance with the given shape and thickness of the future structure, taking into account the width of the foundation, and a trench is dug.
Construction of a trench for a supporting structure
The bottom of the trench is thoroughly compacted with a shovel. The side cuts are given an even geometric shape. A gravel or crushed stone cushion is laid at the bottom of the trench.
Gravel bed at the bottom of the trench
To enhance the strength of the foundation, reinforcing mesh or metal rods are laid on top of the gravel. Reinforcing bars are installed along the contour of the trench in a vertical position to ensure the strength of the structure.
Support wall reinforcement
Formwork
Formwork
Retaining walls made of monolithic reinforced concrete require the construction of a massive formwork structure that can withstand the pressure of heavy concrete mortar.
- Formwork panels are made from boards with a thickness of 3 cm.
- They must be connected horizontally to each other using vertically installed beams with a cross section of 5 x 10 cm.
- The structure is fixed using spacers installed in the ground every 50 cm on both sides of the structure.
- First, install the rear wall of the formwork.
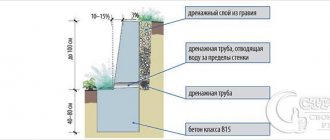
- To avoid deformation and deflection of the frame, vertical metal reinforcement is installed along the wall. At this stage, a drainage system is installed.
Retaining wall drainage
Retaining wall in section
Drainage may differ in location:
- Transverse drainage
Transverse drainage
A hole with a diameter of up to 10 cm should be left in the body of the wall, or a tube with a diameter of 5 cm should be inserted at an angle in increments of 1 m. The drainage is carried out into a nearby water intake.
Cross drain pipe
- Longitudinal drainage
Longitudinal drainage
A corrugated drainage pipe is laid at the level of the foundation, wrapped in geotextile material, which absorbs moisture and allows it to enter the holes of the pipe, from which it is discharged outside the structure.
Laying a longitudinal drainage pipe with your own hands
Each of these options involves laying a drainage layer between the wall surface and the soil. The drainage layer can consist of gravel, broken bricks or coarse sand 7–10 cm thick.
Important! The drainage layer is installed at the stage of soil filling. Instead of fractional materials, you can use a modern drainage fabric made of bulk textiles, then additional pressure on the supporting wall will be eliminated.
Solution
In order for the retaining wall to withstand high loads and be durable, it is necessary to use high-quality frost-resistant concrete mortar. For monolithic thin-walled reinforced concrete structures this is a solution of grade B10/B15, for prefabricated structures - B15/B30.
Frost resistance of concrete:
| Temperature, °C | Minimum frost resistance class |
| from -5 to -20 | F50 |
| from -20 to -40 | F75 |
| from – 40 and below | F150 |
5 days after the solution has set, the formwork is removed. The outer surface of the structure is treated with cement plaster. In a month, the concrete will gain its working strength and will be able to bear the load.
At this stage, the space located on the rear side of the structure is filled. In order for the solution to be of high quality, the instructions for its preparation and the required proportions must be followed.
General recommendations for DIY construction
Do-it-yourself construction is justified for low and medium-height structures. The recommended height of retaining walls for personal plots is in the range of 0.3-1.4 m . Subject to certain conditions, structures can be erected without preliminary calculations:
- The soils should be stable - coarse-grained, loam and clay, sandy loam.
- The upper level of groundwater (overwater) should lie no closer than 1.5 m to the surface.
- The freezing depth should be at least 1.5 m.
- For a wall made of concrete, stone or brick, a strip foundation must be provided. The depth of the foundation should be up to 50% of the height of the ground part.
- To protect against heaving forces, special measures must be taken: drainage arrangement and sand and gravel backfill 40-60 cm thick, cutting off the capillary rise of moisture from the soil.
- When laying a wall of blocks or bricks, it is advisable to make the profile of the structure with an extension towards the bottom. The minimum thickness in the narrow part should be: 60 cm for stone masonry, 50 cm for brick masonry, 40 cm for concrete blocks.
- To extend the service life of prefabricated walls made of stone, brick, blocks and wood, a layer of built-up waterproofing is required on the ground side. For monolithic reinforced concrete structures, the surface is treated with bitumen mastics.
- It should be taken into account that walls with a curved or broken configuration can withstand greater loads than structures with straight outlines.
Filling the space behind the supporting structure
First, fill the drainage soil or lay the drainage fabric, which was mentioned above. After this, the previously selected soil mass is laid in layers of 20–40 cm, which must be compacted as it is backfilled. The top layer is plant soil.
Filling the back wall space
After a few weeks, natural shrinkage of the soil will occur, so it will be necessary to backfill.
Important! You cannot add previously removed peat, silt, soil in which the content of organic and soluble inclusions exceeds 5% by weight, as well as frozen soil.
How to make a calculation?
In order for the structure to fully fulfill its function, at the planning stage it is necessary to calculate its dimensions: thickness and other indicators.
There are SNiP requirements that should be adhered to during calculations:
at 60 cm the wall should be minimally buried in the ground;- from the height of the entire wall, its width should be within 50-70 cm to start calculations;
- the wall should be recessed towards the elevation by 12.5 cm for each linear meter;
- The top cut for a solid wall should be at least 40 cm.
According to the regulations, it is necessary to choose the type of drainage: longitudinal, transverse or combined. For example, if the level of height difference in the area is 130 cm, then the height of the wall according to the standards should be about 2 meters with dimensions for deepening. The calculations also take into account the type of soil, namely the value of its specific adhesion.
Waterproofing the surface of retaining walls
Waterproofing a retaining wall
The rear wall of the retaining structure must be reliably waterproofed using roofing felt or roofing waterproofing material (roofing felt). They are laid in two layers on bitumen mastic. If the soil is dry, then it is enough to treat the back surface of the support with two layers of bitumen.
Treatment of retaining wall with bitumen
Features of device technology on a site with a slope
If the site contains a slope, then the technique will be similar, but at the planning stage you will have to worry about the size and terracing of the site. The owner will have to divide the area into several horizontal zones, and also hire equipment to dig a trench for retaining walls.
A gentle slope can be strengthened with the help of plant roots, but if the slope has a good difference in height, then the construction of a concrete wall cannot be avoided.
For formwork, it is better to use OSB boards, since you will have to bury the base of the wall into the ground as much as possible. Drainage must also be effective: polymer or asbestos-cement pipes are used for its installation. It is better to do transverse drainage with drainage.
Purpose
If the slope of the land is more than 80º, a protective wall must be erected to prevent soil sliding. The building structure is also installed when placing a private house near a reservoir on a steep bank.
The main functions performed by cement-sand support:
- fixing and securing the soil in the required position;
- zoning of a personal plot;
- formation of horizontal planes in the design of landscape design of the territory.
A support installed on a suburban area performs protective, decorative, or both functions at the same time.
Concrete supports can be equipped with stairs, steps, walkways, etc.
Possible difficulties and errors
If technology is not followed, retaining walls may collapse if the master makes a mistake.
The most common problems:
- insufficient foundation depth;
- poor drainage;
- failure to comply with the rules for resting a wall on a hill;
- the height and weight of the wall are too high;
- construction on soft soils with close water levels.
As a result of these errors, the walls may collapse, become covered with cracks, and also collapse at the bottom. If there is not enough experience in construction and calculations, then it is better to invite a team of specialists.
Stone selection
In the garden landscape, one of the most preferred solutions is traditionally a wall made of natural stone. It immediately creates a feeling of beauty and solidity - something that all other materials are somewhat less capable of. Natural material combines perfectly with any plants that are usually grown on plots. Most often we are talking about:
- granite;
- limestone;
- basalt;
- sandstone.
Sandstone, that is, a combination of quartzite and carbonate, is not very strong due to the presence of iron ore. However, its beauty is undeniable, and for many this becomes a decisive factor.
First of all, the walls are made of rubble stone. They are quite massive and require a special, carefully designed connection to the hill. It is recommended to use geotextiles to cover the strips exactly at the seams. The larger the rubble stone specimens, the better suited they are for the initial tiers. At higher levels, lighter elements can be used.
Sometimes artificial stone is also used for work. It can be done on:
- cement-sand;
- plaster;
- quartz based.
Solutions made from wild chopped material are very popular. It varies in surface shape and attachment methods. But it is worth understanding that split blocks vary greatly in size and geometry, even within a specific batch. Therefore, it is very difficult to use them for installing walls, and only trained professionals can perform such work. In some cases, various types of river stone are also used.
This is about:
- sandstone;
- pebbles;
- limestone.
Varieties
There are three different types of retaining walls, differing in purpose and external conditions.
The largest in size are gabions, which are often classified as a type of massive retaining walls, which will be discussed later. The essence of their design lies in stones, which are fastened together and form a single building thanks to a metal mesh.
There are quite a few options for filling the frame:
- Tuff
- Sandstone
- Limestone
- Granite
- Basalt
This variety contains a division into three main groups, differing in scope:
- Low in height used as cladding for bases
- Box-shaped ones are very popular in landscape design; they act as reinforcements.
- Cylindrical ones stand out in their shape; they are used as fastenings to support the banks of reservoirs and in dams.
Thin-wall retaining walls are defined by their shape, which resembles an angle. The material of manufacture is concrete. Unlike massive varieties, this design does its job not due to its own mass, but due to the width of the sole, which successfully holds the ground.
They have a large number of advantages:
- No additional costs for construction, wages for workers and transportation of the object itself.
- During the construction process it does not require too much effort and time, so it compares favorably with massive structures. The reason for the greater popularity of the latter type of walls is that very often thin-walled products are simply not produced at nearby factories, and it will not be possible to fill them on the territory of the construction site itself because the shape is too complicated. This is really a big disadvantage of this type. Despite the fact that there are legislative problems when building massive walls (such structures are regulated by special authorities and cannot be built without a good reason), massive ones turn out to be easier to obtain.
They don’t have many advantages and are unlikely to be suitable for the average citizen. Think for yourself how much financial and physical resources will be needed to work with such huge structures. Moreover, as mentioned earlier, obtaining permission for them is not so easy. There are also problems with transportation.
When constructing massive retaining walls, the fact of the ratio of height and width is very important. For buildings of this size, incorrect calculation of these indicators can result in very bad consequences.
Due to the fact that the higher the building, the more pressure is exerted on its foundation part, the lower section of the wall is made wider than the upper to support the impressive mass.
It is important to use a buttress, because it will provide protection and minimize the negative consequences of a collapse. A buttress is a structure that is located vertically close to a retaining wall. It provides additional support.