When the snow turns white outside the window or the dank gray sky frowns, watering people with its rainy tears, the lack of something bright and summer is especially acute. For example, lush green plants or colorful fragrant flowers. It has long been known that the green “residents” of our homes cope well with the human blues, and they also clean the air in the room. Therefore, a winter garden can be an excellent solution. In a private house, it is much easier to arrange it due to the large spatial possibilities. Where to start, what materials, plants and style to choose - you will learn these and other important aspects from this article.
Winter garden in a private house - how to arrange it?
Greenhouse, winter garden, greenhouse?
The first winter gardens were created by the ancient Egyptians: the richest and most noble of them installed large flowerpots with greenery in their palaces. Over time, the fashion for maintaining a “green oasis” in a residential area appeared among the French and British in the 19th century, and then spread throughout the world. Today, a winter garden in a private house is not uncommon. However, it is important to understand what exactly you are planning to create in your home: a greenhouse, a greenhouse or a real winter garden.
Distinctive features of a winter garden
Table 1. Difference between a winter garden and a greenhouse.
| Design name | Peculiarities |
| Greenhouse | It is placed on the roof of the house or separately from it. Sometimes it may be adjacent to housing. Created for breeding and cultivating fruits, vegetables and flowers, both local and “overseas”. For a greenhouse, it is important to create special conditions, an ecosystem for the comfortable growth of crops. |
| Greenhouse | A mini-greenhouse located separately from the home. Used for growing fruits and vegetables or heat-loving plants. Plant comfort is a priority. Externally, the building is not very attractive, lacks decorations, and is quite budget-friendly. |
| Winter Garden | Most often they are attached to housing and designed in advance. Plants are kept and grown inside, but they are created for people (relaxation, receiving guests). Based on this, the design should have an attractive appearance and be functional inside. |
Useful tips
Before you think about the style and design of the winter garden, you need to understand which plants will be most comfortable in it, and whether you can create the necessary conditions. After all, the price spent on its arrangement will not be small, but the result may be disappointing. It’s good if the construction of an individual oasis is laid out at the design stage of the house, and you can choose which side it will be attached to.
If you are dealing with an existing structure, then consider the following:
- If it is oriented to the south, southwest or southeast, light and heat-loving plants - succulents, cacti, citrus fruits, palm trees, hibiscus, etc. - will grow well here.
- If the windows face west, on a hot summer day they will have to be covered with curtains or blinds, since not a single plant except succulents and cacti can withstand direct sunlight for a long time.
The problem of shading was solved here with the help of roller blinds
- The most favorable location of the winter garden for most plants is with windows facing east. Direct sunlight, not yet hot, will come here only in the morning, and there will be enough light throughout the rest of the day.
- But with orientation to the north it is more difficult; your flowers will not have enough light. But you can use artificial lighting or plant shade-tolerant plants - ivy, fatsia, ficus, hosta, schefflera.
Types of winter garden structures
Before you start creating a home oasis, you need to think through many nuances. First, you need to decide on the type of structure. There are several of them.
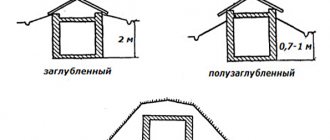
- Buffer garden. This is a room adjacent to the house (often a veranda). It can be entered both from the home and from the yard. Typically, such a building is a connecting link between the street and the house; it has a rectangular or square shape (it can also be corner). They are used not only as a resting place, but also as a hallway or terrace. The advantage of this design is the ease of creation: communications, heating and electricity are easy to install from the house, the building is easy to maintain. The downside is the lack of ventilation, sudden temperature changes (at night in the buffer garden it is much colder), not every plant can survive there.
There is an entrance to the buffer garden both from the street and from the house - Residential garden. A great option for green lovers. This is a full-fledged living space in which you can place a dining room, living room, and recreation area. In such a garden it is comfortable for both plants and people. You can create a residential garden by planning it in advance (if the house is being built), or by placing it in the selected room. The main requirement is the presence of large window openings for sufficient daylight.
There can be a living room in the winter garden - Separate building . It is also called a greenhouse winter garden. If your plot is large, you can afford to put a spacious winter garden on it at a distance from the house itself.
It is important that the place for construction is sunny. It is equipped with heat, light and running water. The greenhouse winter garden can be connected to the house and other areas of the site with beautiful paths. The option is not the easiest and very expensive.
Such a building will decorate the site and an excellent solution for landscape design.
Important: whatever type of structure, it must let in enough daylight for the flowers to grow healthy.
Design features
The winter garden is sometimes located separately from the house, but most often forms one whole with it; in the latter case, the premises make significant adjustments to the design and construction of the house. It is convenient to divide buildings into the following groups:
Buffer room (extension)
The buffer winter garden is organized as a structure adjacent to the house, most often rectangular or corner, although there are other options - square, triangular, semi-oval. Such a room serves as a link between housing and the street; This is the most common arrangement option.
You can also enter it from two sides and use it not only as a relaxation area, but also as an entrance hall, helping to keep the house warm.
A specially erected building, a glazed veranda or terrace can act as a buffer winter garden if it is insulated and connected to home utility systems.
Winter gardens attached to a house are set up relatively easily and quickly, since there is a ready-made wall, and it is not difficult to supply water and electricity from the housing, and arrange heating.
Thanks to its relatively small dimensions, maintaining such a relaxation corner is not difficult. The downside is considered to be insufficient lighting and poor ventilation; Temperature fluctuations will prevent some plants from growing.
Part of a residential building
Placing winter lard in the house can be done in two ways:
- Conceived at the design stage (optimal option). Such foresight makes it possible to equip a room with large windows and a translucent roof at minimal cost; It will be comfortable for both the owners and the plants.
- Located in a finished living space. Even if a corner or spacious external room is allocated for it, adjustments may be required (increasing window openings).
Separate building
This option is practical for large areas; modern technologies will allow you to realize your fantasy. An elegant transparent building will ennoble the landscape and fit perfectly into any style; A round winter garden will look especially good.
A sunny place is chosen for construction, the building is reliably insulated, light and water are provided.
To create a comfortable living environment for plants poorly adapted to the local climate, the room is additionally equipped with special phytolamps. The disadvantage of this design is the cost of its arrangement. The budget will include the supply of communications, the arrangement of the foundation, and in the future - the costs of heating, watering and lighting.
It is convenient to connect the house and the winter garden with a path, the arrangement of which will also require investment.
Choosing a place
If you are planning to place the structure of the future winter garden in a house extension, it will be very important to decide on which side it is best to do this: southern, northern, eastern or western. Each option has certain pros and cons.
- North . The location is not the best, since the garden will quickly release the accumulated heat to the outside. If there is no option to choose the other side, you need to take care of a good heating system.
- South . The good side is during the cold season, when daylight hours are short and there is little sun. On warm summer days, the plants will be too hot and stuffy there, the owner will have to water them more often, provide shading and access to fresh air.
- East . This is the most successful location option: in the first half of the day the plants will be provided with light and warmth, and in the remaining time the flowers will “rest” from the sun. Thus, overheating of crops will be excluded.
- West . The solution is also suitable: the heat accumulated during the day is retained throughout the night. This is good for winter, but in summer you will have to provide additional ventilation and good watering.
Cardinal directions for the winter garden
Ventilation
It is important for plants to receive a constant flow of fresh air.
Choosing windows for glazing cottages - a review of recommendations from expertsDecorating the house with your own hands (step-by-step instructions from A to Z)
- Where to start building a private house
Natural implies the presence of windows. Their area should be at least a quarter of the total area of the walls. Manufacturers offer manual or automatic options. The supply and exhaust system provides air inflow from holes at the bottom of the wall, and outflow through vents.
Mechanical ventilation provides ventilation using fans. Their disadvantages are noise and increased electricity costs.
The maximum effect can be achieved using both systems.
Choosing a form
At the stage of planning a winter garden, it is very important to decide on the optimal form of construction for this room. A separate building can be anything: a sphere, a hemisphere, a cylinder, a cube. However, it is usually rarely installed separately, due to the high price and complexity of implementation.
Most often, a winter garden is part of a living space, in which case its shape also differs. There may be several options:
- a rectangular extension with a pitched roof (the simplest and most popular);
- a structure adjacent to the outer corner of a residential building;
- quarter-polygon (extension to the inner corner of the house);
- structure with a combined roof;
- bay window design;
- L-shaped extension with a gable roof.
Types of structures
Please note: you can design the building the way you need it.
Selecting materials
The inside of the winter garden should be comfortable not only for people, but also for plants. This determines the specific choice of materials for walls and roofs: these structural elements should provide your crops with maximum access to light. Based on this, glass, polycarbonate, double-glazed windows, and sometimes plexiglass are most often used when finishing walls and roof coverings. Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of each material.
Glass
This type of cladding is the most used. Glass is so popular due to a number of significant advantages:
- high load-bearing capacity;
- aesthetics;
- light transmittance (98%);
- fast heat transfer.
These positive properties do not exclude some disadvantages. Glass is a fragile, quite expensive and difficult to work material.
Glass cladding looks impressive
Polycarbonate
The most modern and technological solution, which is popular in the field of construction and finishing. It has many advantages:
- budget;
- easy to process;
- plastic (can be bent);
- moisture resistant;
- resistant to moisture, fungus, corrosion;
- easy.
Please note: polycarbonate has a top layer of protection that does not allow moisture to pass through. This makes it virtually invulnerable to precipitation.
Polycarbonate would be an ideal material if not for some disadvantages:
- low thermal efficiency (good heating will be needed);
- transmits less light than glass (88%).
Polycarbonate sheathing
Double-glazed windows
Today, when creating winter gardens, double-glazed windows have become more often used, despite their high cost and heavy weight. This popularity is due to their high light transmittance (like glass) and excellent heat retention. Also, if your budget allows, you can opt for energy-saving double-glazed windows: they will help significantly save heat.
Double-glazed windows
Plexiglas
As a rule, it is not used as an independent one. Suitable for side walls in combination with other materials. It has a significant disadvantage - it is heavy, which makes you think about a more durable frame.
§ Construction of a winter garden foundation: main points
A big advantage of greenhouses can be considered their relatively low weight, so often existing foundations for terraces are used as a base for them - in the form of reinforced reinforced concrete slabs over 200 mm thick. If necessary, they are reinforced with piles buried below the freezing depth of the soil (that is, at a distance of 1500-1800 mm from the surface of the earth in the case of clayey and loamy soils in central Russia).
If it is necessary to build a foundation from scratch, then various solutions can be used, for example, a foundation made of piles connected by a reinforced concrete or brick strip. Most often, the extension structure is placed on a plinth that rises above ground level. Thanks to the plinth, it will be possible to install heating radiators without damaging the interior of the garden, create window sills on which it is convenient to place flowers, and in addition, in winter, snowdrifts from the outside supporting the walls of the extension will not be noticeable from inside the garden.
Foundation, floor and walls of the structure
The very first stage of creating a winter garden is pouring the foundation of any durable structure, that is, the foundation.
Important: the winter garden room needs a foundation, since heavy pots with plants will create a huge load, and a structure without a foundation will simply sag.
The most convenient and widespread technology for pouring is the strip foundation technology. It is important to follow the basic steps here:
- Apply markings and dig a trench (depth - 50 cm, width - 10-15 cm).
Dig a trench - Install reinforcement (will strengthen the foundation).
- Place a mixture of gravel and sand at the bottom.
Install boards or special thermal insulation on the sides of the trench - Fill the hole with cement (“M-200”, “M-300”).
- Lay a layer of roofing felt (waterproofing) on top of the cement.
Pillow for strip foundation - Wait for the mass to completely harden (15 days).
Attention: please note that pouring and drying the foundation will take 17-20 days.
Next you need to decide on the floor. Initially it is poured with concrete, but after complete hardening it needs to be covered with something. There are several options here:
- ceramic tiles;
- natural stone;
- fake diamond;
- porcelain stoneware;
- boards (rarely).
Based on preferences and budget, everyone decides for themselves what exactly to cover the floor in their winter garden.
Natural stone flooring is beautiful and effective
Foundation and frame
To prevent the winter garden from sinking, it is better to take care of building a reliable foundation. This is a rather labor-intensive and costly part of the entire project - about a fifth of the budget is spent on creating the foundation.
A shallow strip foundation is suitable.
To create it, you can use ready-made reinforced or reinforced concrete blocks 20 cm thick. The depth depends on the type of soil, climate and topography. Instead of ready-made blocks, you can use a concrete solution, but you will have to work hard with the formwork and reinforcement frame.
The floor is made of concrete, then it can be covered with ceramic tiles, natural or artificial stone, porcelain stoneware or terrace boards. The board is also used, but less often.
To arrange the frame, you can use ready-made structures, for example, aluminum or steel profiles, wood.
You can go the more complicated route and build the frame yourself. Brick is used, as well as the same wood, aluminum and steel. After installing the frame, they begin glazing with the selected material.
When arranging the roof, do not forget to provide a slope so that in winter snow does not linger on the roof, increase the load and block sunlight.
Frame and roof
In appearance, a winter garden may look fragile due to its transparency and even some airiness. However, it’s good if she only seems like one. To withstand winds, snowfalls and the scorching sun, the structure must be strong and reliable. For this, it is also important to choose a good frame material. There are many options, let's look at their brief descriptions.
Table 2. Types of frame materials.
| Material name | Characteristic |
| Aluminum profile | The most popular version of the frame has many advantages: - lightweight; - durable; - durable; - not subject to rust. The main disadvantage of an aluminum profile is its high throughput (it does not retain heat), which means you will have to take care of thermal protection. |
| Tree | Wood is often combined with brick, but timber is not a very popular material because: - it can rot; - changes shape and size with temperature fluctuations; - afraid of moisture; - expensive and complicated. If you choose durable and high-quality wood, the building will be durable, but its cost will increase significantly. |
| Steel | An undeniable advantage of a steel frame is its high strength and durability. But the disadvantages are also significant: - very heavy weight; - high price; - susceptible to corrosion. |
| Metal-plastic | Good material, characterized by such advantages as: - resistance to UV rays; — excellent thermal insulation; — high noise insulation. |
| Brick | Brick is used quite often to create a frame base. Pros: - strength; — moisture resistance; — ease of installation; - durability. However, the material is heavy and quite expensive. |
Aluminum profile frame is very popular.
Next, everything will depend on the selected materials and the type of future structure. For fastening, you can use a welding machine (if the frame is made of steel), a screwdriver, a drill, etc. Parts can be fastened with nails, dowels, and self-tapping screws.
After the frame is made, the sheathing begins. The material from which the structure will be sheathed will determine the pitch between the frame guides.
Please note: do not forget about the joints between the walls of the home and the home “oasis” - they need to be treated with insulating foam.
If we talk about the roof of the future winter garden, it is also important to choose the right material. Of all the above, glass is the least suitable: it may not withstand the weight of snow that falls in winter. The best option is polycarbonate or double-glazed windows (2 or 3 chamber).
Attention: do not choose double-glazed windows with a glass thickness of more than 5 mm, since such material is too heavy for the roof.
When arranging a roof, give preference to a configuration with a slope.
A sloped roof will be an excellent solution to prevent precipitation from accumulating on the roof surface and preventing the penetration of light.
Video - Winter garden assembly process
Design form
As for the shape of the structures, if it is constructed from an aluminum profile, its shape can be:
- square;
- rectangular;
- semicircular;
- polygonal.
Here it is worth taking into account the specifics and general style of a residential building. As for the roof, it can be made single- or double-slope, domed, and so on.
Advice : when building a winter garden, it is best to choose full rather than partial glazing. Such an extension will transmit the sun's rays as much as possible, which will significantly reduce the cost of heating the room.
Choosing a heating system
Sunlight is the source of life and heat for plants. However, in cold weather, for their existence and growth, as well as for the comfortable stay of people in the winter garden, it is necessary to install an optimal heating system. The choice will depend on the following factors:
- room area;
- plant species;
- frequency of people being in the room.
The assortment of modern stores allows you to make the right choice from many existing options.
Operating principle of an electric convector
Table 3. Types of heating devices and systems.
| Name | Device properties |
| Electric heaters | — easy to install; - mobile; — quickly heats the air; - available; — high electricity consumption; - dry the air. |
| Split systems | — uniform and fast heating of the room; - ability to regulate temperature; — do not affect air humidity; - high price; — electricity costs; - not suitable for northern regions. |
| Water heating (from the house heating system) | — temperature stability; — minimal costs; — identical microclimate; - installation difficulties (it is better to do this at the initial stage, when the house is still under construction). |
| Warm floor | — uniform heating; — convenience and comfort; — prevent freezing of the floor and walls; - high price; — complexity of repair; - Difficult to install. |
| Ural Federal District | — heat the room evenly and quickly; — it is possible to adjust the temperature; - will not affect air humidity; - are expensive; - not suitable for large rooms. |
| Heating from the stove | - low cost; — uneven heat distribution; — danger of fire (in the absence of a person in the room). |
Heating systems can be easily combined with each other
What else?
- Don’t forget to find out in advance what kind of soil the selected plants will need, what fertilizers you will need to buy, and how much money will be spent on providing all engineering systems.
- Also, don't forget to consider the location of the outlets.
- When choosing furniture for a recreational area, give preference to products made from natural materials: wood, rattan, wicker.
- Research whether the selected plants can be adjacent to each other. Also decide in advance how you will plant all the varieties.
Choosing a ventilation system
Any room needs regular ventilation, and the winter garden needs constant ventilation, because the green “residents” of your cozy corner need fresh air. He can get from the street inside (and vice versa) in two ways.
- Natural . Simply put, windows need to be provided with vents and transoms. This is a cheap option, there is little noise from such ventilation, and by opening and closing the holes you can easily regulate the air flow. However, such a system will fail in the warm season, when the temperature difference is minimal.
- Mechanical . Involves the use of technology, such as fans or more complex systems. They will create an excellent microclimate, but noise may interfere with your relaxation. It is also worth considering installation costs and electricity bills.
Ventilation diagram in a house with a winter garden
Climatic conditions
So, the construction of the garden room has been completed, all that remains is to connect communications to the building and plant the plants. In order for flowers and plantings to feel comfortable, it is necessary to take care of creating an ideal microclimate.
When a winter garden is located in a house, it is much easier to monitor the climate in it, and it is, therefore, as close to comfortable as possible.
If the corner of nature is located outside the living space, then in this case it is necessary to take care of normalizing the following parameters:
- Air parameters.
- Light.
- Air exchange.
- Heating.
Choosing lighting
The walls and roof of the winter garden are sheathed with transparent material, which means there should be no problems with lighting. Still, plants often need additional light. There are a large number of sources of artificial lighting: mercury, sodium, fluorescent, LED, metal halide, phyto-lamps and incandescent lamps. Of these, fluorescent ones are the most popular because they save energy, provide excellent illumination and have low heat dissipation.
Phyto-lamps are especially good: they have a positive effect on photosynthesis. The downside of this option is its price.
Think about how you can protect your flowers: curtains, blinds, awnings, awnings
Don’t forget that too much light is also bad.
Protecting the winter garden from strong solar radiation
When planning garden lighting, you should take into account the opposite effect of its overabundance. In summer there is too much light, and in order to prevent its harmful effects, the garden must be protected. Measures to protect the winter garden can be divided into two types:
- internal protection – blocks up to 40% of light
. These are curtains and blinds made of various materials. Typically fabric, plastic, bamboo or aluminum are used. The latter should not be used, because the metal heats up quickly and gives off heat for a long time. This affects the overall temperature regime. In addition, they make noise and vibrate when the fan is running.
- external protection – blocks 70-90% of light
. These are awnings, awnings, for the production of which a special fabric with a reflective surface is used. External protection is preferable because the wall material does not heat up and the overall temperature in the garden does not increase.
Selecting and combining plants
When choosing plants, you will have to rely not only on your own preferences and taste. It is very important that the cultures are combined with each other, because they will be in the same room.
According to zones and conditions, plants are divided into:
- tropics;
- subtropics;
- desert;
- humid tropics.
It is unlikely that you will be able to combine flowers from different climatic zones, so make sure that the requirements are approximately the same.
Do not forget about the location of pots with plants: the sunny side is an excellent place for light-loving crops
About watering plants
Is your garden small and compact? Then, in order to water all the flowers, you will need a basic watering can, a spray bottle and a schedule for adding water. But in the case of a larger room, watering can become a problem and take a lot of effort and time. An excellent solution is a drip system: pre-installed hoses will ensure a regular flow of liquid into the substrate, and special sensors will be responsible for the humidity level.
For additional humidity and beauty, you can install an artificial pond in the garden.
Garden design: zoning and style
Upon completion of construction and installation work, it becomes necessary to plan the interior arrangement of the premises. This is where such an effective technique as zoning comes to the rescue, i.e. dividing the winter garden space into functional zones. There are several of them.
- Decorative . This is a place reserved for plants and various decorative elements (fountain, aquarium, figurines, etc.).
- Service . Fertilizers, equipment, and other things useful in caring for flowers will be stored here.
- Recreational – recreation area. For its arrangement, sofas, armchairs, hammocks and tables are used.
- Communicative . Such a zone exists in large rooms. These are places for alleys, paths, paths that will connect all other areas with each other.
Zoning a winter garden
When it comes to decorating a garden in any style, you should also start from your own tastes. The common features of a particular style will help create an aesthetically attractive cozy corner.
- Classic. This is the predominance of symmetry, pompous figurines in the form of living creatures, people, fountains in the form of geometric figures.
Winter garden in a classic style - High tech. A winter garden in this style is characterized by a combination of metal, concrete and plants, laconic and precise lines.
High-tech style - Eco style. Naturalness, naturalness. Select plants that are typical for your region. Figuratively speaking, this is a piece of the garden “under the hood” - this should be the impression of your winter garden.
Eco style - Country. Similar to the previous style. These are natural decorations (vines, stumps, clay pots) and the simplest possible local crops.
Country - Japanese style. Very beautiful, with his own philosophy. The main elements are stones, earth/wood, water.
Winter garden in Japanese style
Details you shouldn't forget
In conclusion, we will give some tips that may be useful in planning and arranging a home “oasis”:
- calculate the approximate cost of the planned structure;
- determine the location of outlets in advance;
- choose natural materials for furniture (wicker, rattan, wood);
- plan methods and methods of planting;
- take care of fertilizers;
- Shade the garden in hot weather.
A mirror will help to visually enlarge the space of a small room.
Master Class. Example of winter garden construction
So, now you know about all the winter garden systems and its internal structure, and therefore you can proceed directly to the construction process.
Important when building a winter garden
Step one . First, determine which side of the house the building will be located on. It is better to give preference to the western or eastern wall. Also, the winter garden can be located from the south, but in this case a serious ventilation system will be needed to maintain the optimal temperature inside in the summer.
Step two . The construction site is cleared of plants, stones and debris. After this, the foundation is poured - a shallow shallow foundation.
Step three . The lower frame frame is mounted on the base, and there must be a waterproofing layer on it. The position of the lower harness is controlled using a tape measure, stretched ropes and a building level.
Installation of the bottom trim
Step four . Horizontal/vertical elements of the future frame are mounted, which will serve as the walls of the garden. It is important that all connections are secure.
Installation of vertical frame elements
Installation of horizontal frame elements
Step five . Next, the top frame is mounted and the roof beams are installed. It is important that all wooden elements used are pre-treated with an antiseptic impregnation.
Installation of the top trim
Installing roof beams
Step six . Rubber sealing profiles are prepared and glazing of the structure begins. Sheathing elements are transferred using vacuum suction cups - this is not only safe, but also convenient.
Glazing of the winter garden
Glazing process
Step seven . On the outside, the seals are covered with an aluminum profile, which is necessary for protection from moisture and sunlight.
Glazing is almost complete
Installation of aluminum profiles
Step eight . The cornice profile is installed. It is advisable to additionally equip it with a drain.
It is advisable to supplement the cornice profile with a drain
Step nine . When the construction of the garden is completed, water and electricity are supplied to it, and irrigation and ventilation systems are equipped. Places for plants are being marked out and the interior decoration of the winter garden is being carried out.
On a note! As a result, you will get a comfortable and beautiful room where you can spend your free time surrounded by your favorite plants throughout the year.
- 3.1. Location on the cardinal points.
- 3.2. Types of structures.
- 3.3. Winter garden design.
- 3.3.1. Ventilation and heating. Ventilation.
- 3.3.2. Static strength of the structure.
- 3.3.3. Glazing.
- 3.3.4. Roof.
- 3.3.5. Blinds.
- 3.3.6. Heating.
- 3.4. Winter garden interior.
- 3.4.1. Automation system.
- 3.4.2. Microclimate.
- 3.4.3. Lighting.
3. Construction of winter gardens.
3.1. Location on the cardinal points.
A winter garden can be built oriented to any side of the world. The orientation depends on the purpose of the garden: its use for relaxation and communication with nature or for work (office, studio).
The architecture of the house itself and the characteristics of the site on which it stands are of no small importance.
Location south
– this orientation is advantageous from the point of view of energy saving (greenhouse effect). Therefore, when using such a garden as a living room, it becomes necessary to install ventilation and shading systems in it, otherwise the room on sunny days will turn into the tropics, especially in summer.
With a northern location
The winter garden also saves energy due to the fact that wind and cold do not reach the walls of the living area. The north side is ideal for creating an office or greenhouse due to the uniform diffused light.
You will be pleased to have breakfast if your winter garden is located on the east side
, where the sun is already shining early in the morning. As a rule, there is no serious overheating here during the day, but ventilation and shading are still necessary.
In the winter garden facing west
, it’s nice to spend the evenings, because... During the day, it collects solar heat and in the evening gives it to its visitors.
3.2. Types of structures.
There are several volumetric-spatial structures of the winter garden. The simplest of them is a three-beam gazebo
- Easily adapts to any room.
The five-ray composition
, which is more rounded, has a beneficial effect on the human psyche.
A gable extension
(the so-called traditional style in Russian architecture) goes well with our roofs.
The four-slope gazebo
is connected with its slope to the main wall of the building using a special gutter.
, a P-shaped gazebo
is best suited .
It has a universal design, which makes it possible to create an optimal lighting design for a modern building of almost any architectural modification. The T-shaped garden
is strictly symmetrical, because...
the flow of light from the central part evenly fills the volumes of the side rooms. A Mediterranean gazebo
(or solarium), which has a pitched roof, serves as a decoration for low buildings.
The supporting structure is made of metal or wood. Its main purpose is to ensure the strength of the winter garden frame. The most acceptable option is to use aluminum alone or in combination with wood. Aluminum is a natural material that does not contain impurities harmful to humans. Thanks to resistance to ultraviolet rays, sun and heat, strength, lightness, durability, impeccable appearance and a rich range of colors of polymer coating, aluminum building structures are indispensable for constructing home gardens.
3.3. Winter garden design.
A winter garden is a rather complex structure, and in order for it to bring warmth and joy for many years, it is necessary to develop a high-quality project. Only professionally designed and built, it will allow simultaneous solution of architectural, planning, economic and energy problems. The main characteristics of any winter garden are:
– design safety,
– protection of the internal space from cooling and overheating,
– rigidity and strength of the frame,
– optimal light transmission,
– high resistance to extreme weather conditions.
It is very difficult to create a winter garden yourself, without special training and experience in the field of landscape design. In order for the winter garden to bring joy and become the most favorite place in the house, you must, first of all, clearly imagine what it should be like and formulate your wishes to the architect-designer.
Since only about 30% of winter gardens are designed simultaneously with the house, and 70% are added to existing housing, today the most common type of winter garden is a glass extension to the house, connected by doors to the living spaces. Although the most successful and beautiful winter gardens are those laid out by the architect at the design stage, when all aesthetic and technical issues can be taken into account.
The first and main task of a winter garden is to expand the living space. Most often it serves as an extension of the living room or dining room. In this case, its convenient functional connection with the corresponding rooms of the house (for example, the kitchen) must be ensured.
The attached winter garden must occupy at least 12 square meters. meters, and even better – from 15 sq. meters. This is due to the high cost of one square meter of space, and the difficulty of harmoniously combining plants, furniture and free space in the interior of a “green” living room.
The height of the room in its middle part should be at least three meters, but an ideal winter garden from the point of view of interior beauty can occupy two floors.
The effectiveness of a winter garden depends not only on its size and location, but also on the slope of the roof. An ideal winter garden should have a roof slope of 30-40 degrees, as in this case it absorbs solar energy best. The steeper the roof, the better the rain washes away dirt and snow.
You should carefully consider the layout of the winter garden, highlighting the main functional areas:
– recreation area,
- the garden itself,
- a place of communication.
The most successful compositions are when the green space “flows” into the space of the house. In this case, it is better to equip a resting place in the room adjacent to the garden.
Stages of designing a winter garden:
1) definition of the image;
2) creation of a compositional and constructive layout of the winter garden space;
3) selection of heating and ventilation systems;
4) calculation of natural and creation of artificial lighting;
5) determining the degree of moisture required for plants;
6) determination of the optimal composition of soil mixtures;
7) careful consideration of the daily process of caring for the winter garden.
Modern devices that simplify the care of the winter garden - lighting systems, automatic systems for maintaining temperature and humidity conditions, ventilation - are designed simultaneously with the selection of plants and the creation of a scheme for their location in the winter garden space.
3.3.1. Ventilation and heating. Ventilation.
For the well-being of people and plants in the winter garden, relative humidity is important. Most “living things” are comfortable when it is 40-60% (only tropical plants need 80-90%). The level of humidity is directly related to temperature: even minor changes in temperature cause air masses to move and collide with each other. And when warm, humid air comes into contact with cold surfaces, condensation occurs, glass and profiles “fog up.” Therefore, the design of the winter garden itself includes measures to prevent the formation of condensation. For example, in aluminum profiles there are thermal breaks made from frost-resistant polyurethane, polyamide or EPDM inserts. They divide the profile into two parts, so that the cold part, located outside, is separated from the warm inside. But even with good thermal insulation of the racks and normal heating, it is hardly possible to completely avoid condensation if you do not think through the ventilation system. It is this that helps reduce air humidity and provides another condition for a favorable microclimate in the winter garden - the flow of fresh air.
Ventilation is natural
and
forced
. Natural operates strictly in accordance with the laws of physics. As you know, air, when heated, always tends upward, towards the ceiling. Therefore, in the lower part of the walls of the winter garden there are opening doors through which cold fresh air enters the room. In the roof part, as close as possible to the ridge, special hatches are installed to release excess warm air. The difference in height is a prerequisite for the circulation of air masses.
Another option for natural ventilation is that outside air enters the room through grilles or vents located at floor level, and exits from the flaps at the top of the “transparent” walls. The holes should be located evenly throughout the entire volume and diagonally to each other, only then will the air flow “fly around” the entire winter garden. Otherwise, convection will occur unevenly - in one corner or another. A similar system is suitable for glazed rooms whose width is over 6 m or which have a small roof. But if the roof is large and high, you cannot do without hatches on it. Ventilation grilles, which are mounted in the parapet, allow you to ventilate the winter garden without opening the window. In the West, they are common largely for security reasons: at night, a person will not be able to get inside through a small grille, and fresh air is easily accessible. In our country, cottages are most often located in protected areas, so bars, which also have to be closed for the winter, are not as successful an option as doors.
The number, dimensions, and location of ventilation holes depend on many factors, including the configuration, volume of the winter garden, its orientation to the cardinal points and even the wind rose. Typically, the area of sashes and hatches is 5-10% of the total glazing area. But the more opening elements you install (special frames, hinges, locks or handles), the higher the cost of the structure will be.
Natural ventilation can be automatic.
It is often included in the overall microclimate maintenance system, working with lighting and heating. In a large winter garden it is worth installing forced ventilation. These can be supply and exhaust systems that take air from the street, or air conditioners that “work” with the air already available in the room. Hair dryers look very nice in the winter garden - blade fans that are mounted under the ceiling. The advantage of mechanical devices is that they allow you to smoothly regulate the intensity of air exchange and always “mix” the air evenly; minus - energy consumption and non-operation in case of power outage. Yes, it’s strange to breathe air conditioning air in the summer, and not fresh air from the street. Therefore, experts recommend always combining forced ventilation with natural ventilation. Heating.
The winter garden can be heated in different ways:
– radiators connected to central heating,
– autonomous electric heating devices,
– using air heated by an air conditioner,
– “warm floor” – both electric and liquid coolant.
Combinations of these systems are often used (one should not forget about infrared radiation that heats the air). In principle, it is possible to calculate the number of radiators required for the structure. To do this, it is necessary to take into account the total area of the room, the area of “transparent” surfaces and the thermal characteristics of the enclosing structures (profiles and light-transmitting elements). However, the temperature inside the winter garden is also influenced by other factors, for example, the amount of thermal radiation or the location of the structure. You should also pay attention to ensure that you yourself do not disrupt the air movement, thereby reducing efficiency, by blocking the radiator with the back of the sofa, installing a window sill above it, etc. In addition, most modern radiators have power control. Therefore, in many cases, heating calculations can be simplified: calculate the number of radiators needed for a closed room of the same area, and install them twice as many. It is recommended to place radiators around the perimeter of the winter garden. Then the room will be heated evenly, and “stagnant zones” will not appear. Moreover, warm air reduces the formation of condensation on cold glass or profile surfaces, but only if the air is moving. Therefore, it is impossible to do without ventilation in a glazed structure.
3.3.2. Static strength of the structure.
In order for the winter garden to continue to be cozy and safe over the years, the structure must meet all stability requirements. The winter garden is a system thought out to the smallest detail. Some companies calculate the strength of each element of the “future” structure (in accordance with SNiP 2.01.07-85 “Loads and Impacts”), others work with “ready-made” systems, the strength of which has long been calculated and time-tested. But in any case, designers rely on the same static principles, some important points of which should be noted.
Three types of loads act on the supporting elements of the structure: snow, wind and own weight. The ability to withstand them varies among the materials from which winter garden profiles are made. The modern market offers profiles made of aluminum, plastic (PVC) and hardwood. Many systems are combined, such as plastic-aluminium, aluminum-wood or aluminum-steel. Systems made entirely of wood are very rare in Russia. The fact is that wood is too sensitive to atmospheric influences, and besides, a winter garden made of this material is a one-piece construction and very expensive. In principle, the size of the winter garden has little effect on the choice of material for the profiles. However, depending on the size of the structure, the cross-section of the racks will be different: for example, aluminum ones will be thinner, plastic ones will be thicker. And a large winter garden will need more PVC profiles than aluminum posts. And with a certain size, the winter garden will definitely need a frame to support the roof. The strength calculation of a winter garden begins with identifying the most loaded racks and crossbars. First of all, this concerns roof elements. It is on their “shoulders” that the main snow and wind loads fall. If the angle of the roof is less than 20 degrees, then take the maximum weight of the snow cover - 140 kg per 1 sq.m, and this means not so much the load on the beam itself, but the load on it from the double-glazed window, abundantly “strewn” with snow. In near-wall zones, valleys or other places where snow pockets can form, which means the expected load can increase, a correction factor (turbulence, pulsations, etc.) is added to this value. If the slope is more than 60 degrees, then the snow melts off such a roof and is not taken into account. In winter gardens of a “substantial” area, corner zones are identified, the wind load on which also increases by 1.5 - 2 times. If the roof is in the form of a tent, the aerodynamic coefficient is lower. We must remember that even that part of the structure that does not seem to be blown by the wind is still subject to load: the wind does not move directly, but with a swirl, as a result, a lack of air pressure is created, which is compensated by the pressure inside the building. Hence the impact on the structure in the direction from the room to the street. After determining all the loads acting on a specific rack or transom, they are summed up. Next, it is calculated how much this load-bearing element will bend. The maximum deflection value is 1/300 of the length of the rack or crossbar. Some sources recommend limiting deflection to 8 mm. This figure is due not only to considerations of strength, but also to visual perception. If, according to calculations, the deflection will be greater, it is necessary to increase the profile section or make a supporting frame.
An important point is the expansion and contraction of the structure under the influence of temperatures. Mechanical loads on it are also possible during the “shrinkage” of the building, because a winter garden is most often an extension that is lighter than the main building and, as a rule, has its own foundation. Therefore, in most winter garden systems, all joints are sealed, but at the same time flexible, allowing for play. Increased attention is paid to the places where the extension is attached to the base and to the wall of the house. Double-glazed windows have to take on the same loads. But the double-glazed windows that form the roof of the winter garden have special requirements - the safety of the inhabitants of the structure also depends on their strength. Therefore, in such double-glazed windows, the top glass is usually tempered
, and the bottom must be
laminated
or
triplexed
.
Tempered
The glass is processed at high temperatures with sharp cooling, due to which it becomes 4–5 times stronger than usual.
Laminated glass
is glass coated with a special film, while
triplex glass
is several glasses joined together with a film. Such glass breaks, but the fragments do not scatter throughout the room, but remain glued to the film. If you plan to make a roof from polycarbonate panels, then, among other things, it is necessary to provide for significant expansion of this material under the influence of temperatures. It is obvious that the design of a winter garden should not only be statically strong, but also optimal in size, beautiful and, if possible, economical.
3.3.3. Glazing.
Double-glazed windows are most often used as a translucent material for facades and roofs of winter gardens. The climate in the room depends on the number of chambers: behind single-chamber “walls” it is colder, behind two-chamber “walls” it is warmer. But an ordinary double-glazed window, regardless of the number of chambers, is not able to adequately retain an additional source of heat in winter - solar energy. In summer, it will also not be able to prevent the free penetration of heat rays into the garden. The reason for this is the physical properties of glass. Glass transmits part of the incoming solar energy, and reflects and absorbs part. Ordinary glass absorbs long-wave infrared radiation and short-wave ultraviolet rays, while transmitting visible light and short-wave thermal radiation almost unchanged. The rays, getting inside, heat the walls, floor, and interior items, which in turn themselves begin to “heat” the room. But if ordinary glass is installed in a double-glazed window, then it, while easily transmitting useful radiation, just as easily releases it outside.
To improve the thermal insulation of the winter garden, energy-saving glass is used. A low-emission coating of tiny metal particles that cannot be seen with the naked eye is applied to one of the surfaces of such glass. In winter, such a coating reflects “warm” rays back into the room, with almost no effect on the optical properties of the glass. There are two main types of coated glass: K-glass and E-glass (sometimes called E-glass). The latter retains heat better, but its coating is “soft”, so this glass is more labor-intensive to produce. As part of a double-glazed window, the coating is usually located on the side of the glass that faces inward. Sometimes home owners, wanting to improve the climate in a glazed extension, install walls made of double-glazed windows, where two glasses at once have a low-emissivity coating. This expensive solution increases the thermal efficiency of the “walls,” although the bulk of the radiation is reflected by the first glass. In summer, the glazed surface, on the contrary, is the main source of excess solar radiation. But K- and E-glasses are also effective in summer: they reflect rays, therefore, together with other sun protection measures, they improve the well-being of the “inhabitants” of the winter garden.
The facades of the winter garden can be made of solar control glass (most often as part of a double-glazed window). These are tinted glass or coated with films (often mirrored) that absorb, but almost do not reflect solar energy and ultraviolet radiation. They will not be able to replace glass with low-emission coating, but they will protect it from prying eyes. The main colors of such glasses are bronze, gray, green, blue, brown. It should be remembered that due to the high level of thermal energy absorption and, as a result, strong heating, such glass cannot be used in an untempered form. Sometimes, instead of spraying, a special film is used, which is stretched between double-glazed windows, forming an additional chamber.
3.3.4. Roof.
Through the glazed roof, even more thermal radiation penetrates into the winter garden, since the higher the angle of incidence of the rays, the “hotter” it is in the room. Therefore, the double-glazed windows from which the roof is made must have very good thermal characteristics. But it is not always technically possible to install a double-glazed window on the roof: this is a large load on the profiles, and structures made of some materials (mainly plastic) are not able to withstand it. Sometimes it is necessary to radically change the shape of the structure, because... deformations are possible. In such cases, multi-chamber polycarbonate is used. This polymer material, as a rule, is cheaper than double-glazed windows, has a low weight (from 1.5 to 3.5 kg per 1 sq. m), is very durable and has good thermal insulation properties (good thermal insulation properties are characteristic only of cellular polycarbonate panels with a thickness of at least 25 mm). Disadvantages include the inability to reflect solar radiation. Bronze or matte white polycarbonate protects the eyes from bright light (like sunglasses). Transparent panel - no. But regardless of the color of the material, infrared radiation easily penetrates under the roof in summer, and easily passes through it in winter. Films with a metallized surface have been developed specifically for polycarbonate, which have good performance in reflecting “warm” rays. But light-transmitting facades and roofs of winter gardens are not always able to cope with the sun on their own.
3.3.5. Blinds.
To improve the microclimate, blinds are installed. Films and coatings protect actively, reflecting infrared radiation before it enters the room, and blinds protect passively, absorbing the rays and preventing the heating of objects inside the structure. Another function of blinds is to protect your eyes from bright sunlight and protect from prying eyes in the evening. In addition, they are able to reduce the flow of ultraviolet radiation, keeping the colors of interior items bright. Blinds are external
and
internal.
The external ones are interwoven fiberglass threads covered with a vinyl sheath, aluminum or plastic plates. These blinds diffuse and absorb solar radiation before it reaches the surface of the glass (or polycarbonate), without interfering with the flow of daylight. External blinds are a characteristic attribute of a European winter garden, but in our conditions they are not entirely practical: after heavy rain and wind, the blinds will get dirty. In addition, they are very problematic to use in winter.
Domestic
blinds, on the contrary, are perfectly protected from any external influences. The materials for them are fiberglass covered with a vinyl shell, polyester with a vinyl shell, fabric made of acrylic fibers, plastic, aluminum plates or the thinnest wooden slats. There are a great variety of colors and shades of these materials, and over time they practically do not fade. Internal blinds also absorb solar radiation, but when they heat up, they themselves heat the air in the room. This is especially true for dark-colored blinds. There are blinds with metallized coatings that do not absorb, but reflect heat rays, increasing the level of comfort inside the winter garden. However, blinds for ordinary windows are not suitable for the roof of a winter garden, not only because the glazed openings come in very complex shapes, but also because the blinds are attached to them using special structures. Installation of blinds is complicated and requires additional costs, because they must move without sagging, and the fastening mechanisms must not be noticeable. If instead of blinds you decide to hang curtains in the winter garden, do not forget that the ceiling will still have to be covered with something. Blinds are controlled both manually - with nylon threads or poles, and using electric drives, sensors and remote controls.
3.3.6. Heating.
There are several types of winter gardens based on the type of heating:
– unheated
– heated from time to time
– heated
The heating option determines its technical design, choice of building material and temperature conditions, which, in turn, determine the subsequent selection of plants.
How to use the winter garden depends on the heating option:
1. Use all year round as a living space.
In this case, the winter garden must be heated.
There is no energy loss due to special thermal insulation glazing. When using a winter garden as an additional living space, the thermal insulation regulations must be taken into account, i.e. calculated values for thermal insulation for windows and sliding (terrace) doors. A heated winter garden improves the average heat transfer coefficient of the entire house according to its external area. 2. Use as a buffer and solar collector
If we are talking about a winter garden, as a transition zone between the external and internal environment, then there is no need for additional heating. The glass extension acts as a thermal buffer and solar collector. It is only necessary to ensure that the resulting heat is transferred to the house itself. In order to operate according to this principle, a winter garden needs a large accumulating mass that collects and releases heat. Therefore, it is not recommended to cover the floor with carpet, which does not protect the floor of the winter garden very well. There are no special requirements for glazing. In most cases, simple glazing is sufficient. But a double-glazed window is still recommended, because... it prevents the formation of melt water and ice. A properly constructed unheated winter garden improves thermal insulation and thus reduces heating costs. This garden, of course, cannot serve as a living space all year round.
3.4. Winter garden interior.
The walls of the winter garden are usually made transparent - made of glass or plastic. The floor can be tiled or wooden, but must be covered with a polypropylene carpet or other non-rotting material. It is better to choose plastic furniture for the room, and the ideal option is wicker furniture.
Winter gardens can be divided into:
– small (20-30 sq.m.) – simple layout, includes three main areas: plants, paths and a place to relax;
– medium (30-50 sq.m) – in addition to the main zones, design elements are used;
– large (over 50 sq.m.) – landscape style techniques are used: tiers, podiums and terraces, a swimming pool, fountains, large volumetric compositions of plants, sculptural compositions are placed.
A popular practice is to use mini-sculptures, statues, decorative fountains, mini-waterfalls, aquariums, alpine slides, and floral compositions in home garden design. But the main element of interior design is, of course, plants. There are a number of criteria that should be followed when selecting flowers for the garden. For example, plants that are very sensitive to direct sunlight should be located in the shade of more light-loving plants.
With all the variety of choices, do not forget about the concept of the winter garden - it must be made in one strictly defined style.
Construction of a real “winter garden” is an expensive pleasure. Suffice it to say that on average the minimum price per square meter of construction is $300. And this is the simplest option.
In general, a winter garden is the most perfect and most complex form of interior landscaping in architectural, engineering and artistic terms.
3.4.1. Automation system.
To avoid problems associated with temperature fluctuations, low or high humidity, insufficient or excessive lighting, a modern automation system is used, controlled by a universal controller.
It can be used to control absolutely everything - from irrigation to emergency lighting. With its help, you can change the temperature by turning heaters on and off, maintain the desired humidity (using a humidifier and air conditioner) and lighting (using lamps and controlled curtains).
The controller “knows” the norms and timing of watering each plant, and “distinguishes” with what kind of water – cold or warm – a particular plant needs to be watered. In areas that require different degrees of watering, you can adjust the duration of watering by installing its own rain sensor in each. The sensor is based on a hygroscopic disk, which expands when water enters and opens the contact; its triggering threshold is 3, 6, 13, 19 and 25 mm of precipitation. Using technical means, this threshold can be increased or decreased by inserting a plastic funnel or closing part of the hole for collecting water. Returning the contacts to their normal (closed) state depends on environmental conditions - humidity, light and temperature. These conditions determine how quickly the contactor's hygroscopic disk will dry out. Then the contact closes - the soil is ready to receive moisture, and the controller “decides” when it is better to water the garden - immediately or a little later.
The controller also “monitors” the presence of people - if the motion sensors, which are also used to automatically turn on the backlight, give a signal about the presence of the owner - it is better to delay watering a little to avoid troubles.
Automation can also control fountains in the garden - the dynamically changing pattern of jets has a positive effect on the human psyche.
3.4.2. Microclimate.
The inhabitants of the winter garden (both plants and people) need a certain temperature and humidity, sufficient lighting and a flow of fresh air to feel good. Maintaining a normal temperature (on average 20-22 degrees for a person) is the most important and difficult task, since a winter garden is a structure made of glass or other light-transmitting materials, which means that in our weather conditions in winter you will inevitably have to deal with hypothermia, in summer - with overheating of the air inside the structure.
If we talk about the difference between growing plants in open ground and indoors - be it a private winter garden, greenhouse or industrial greenhouse - the advantages of the latter lie in the ability to create an artificial climatic environment, which is called a microclimate.
Maintaining a particular temperature regime that meets the requirements of the plants being grown, humidity directly related to it, light intensity, and sufficient air exchange is the main thing that is required in regulating the microclimate. After all, a winter garden is a complex ecosystem, and not just a decorative interior design. And each type of plant has a certain optimal temperature and humidity.
3.4.3. Lighting.
Lighting of the winter garden is very important. Firstly, lighting that provides comfortable conditions for residents and guests in the evening and at night. This is a standard set of chandeliers, lamps, sconces, and floor lamps. Particular attention should be paid to decorative lighting. Directional or spotlights will highlight the beauty of plants and the originality of the design. There will be no problems with this either; the selection of them on sale is simply huge. Light sources are not fixed and can move. Secondly, and more importantly, it is illumination of plants from a physiological point of view, if there is no glass roof and the plants are located away from windows. In this case, lamps with special lamps designed to illuminate plants will help. It is advisable to illuminate plants no more than 12 hours a day during the daytime, without disturbing their natural growth cycle. This, of course, is not all the subtleties in caring for a winter garden, but if you wish, it is quite possible to master these intricacies.
Table of contents
Gas boiler room on the roof - find out more.