The cutting down or replanting of green spaces on the territory allocated for development is determined by legislative norms for environmental protection. In accordance with the rules for carrying out work, the developer must obtain a special permit - a logging ticket, in the presence of bushes and trees that are subject to destruction or replanting. This requires dendrological research. In this article, we will get acquainted with the composition of these works, and also consider what a dendroplane is (examples of ready-made plans will be given for maximum clarity).
Conducting dendrological research
Before starting construction design on a site with existing green spaces, it is necessary to carry out dendrological studies, including drawing up a dendroplan and a counting sheet indicating data on the location of all trees and shrubs growing on the territory. The drawing can be combined with a tree-by-tree topographic plan (scale 1:500). Without carrying out dendrological surveys, it is impossible to obtain a felling permit, which grants the right to cut down or replant plantings on the territory of future development.
Engineers are faced with the task of studying in detail the age, species and type of trees (shrubs), as well as estimating their cost. Specialists conduct research in accordance with regulatory documents and develop the necessary recommendations to minimize damage to nature during the construction (restoration) of objects. Upon completion of the work, a dendrological plan is drawn up and a subsequent examination is carried out. There are standards for the distance between objects and green spaces, which the developer must adhere to. This is impossible without dendrological research.
It is recommended to draw up a dendroplan simultaneously with geological surveys. If this drawing is missing, it is simply impossible to maintain the gaps between planting areas, as well as the standard distances between the axes of plants and buildings. A well-designed dendroplan allows developers to make informed decisions on the optimal placement of an object on the ground in relation to existing green spaces in order to comply with state requirements for environmental protection.
The importance of the balance sheet
The accounting sheet is a mandatory document that is included in the dendroplane kit. It contains a list of planted crops that are most suitable for a given land plot. The landscape designer must take into account the wishes of the customer, as the most interested and influential person.
The dendroplan and the balance sheet, as a rule, cannot exist separately, but form a single whole. The latter sometimes acts as an annex to the explanatory note, which is drawn up for the general plan of the personal plot.
The following data is entered into the accounting sheet:
- variety, type and decorative forms of trees planned for planting;
- individual number of each tree or shrub;
- characteristics of each type - height, type of root system, decorative features;
- crown projection;
- number of seedlings of each type;
- name of the plant (in national and Latin languages).
The recording of landings in this document is made in a certain order, that is, in groups. The first group includes coniferous species, the second – deciduous, then – fruit trees and vines.
Such documentation allows you to plan in advance the purchase of the necessary varieties and types of plants, avoid mistakes inherent in amateur gardeners, and also save your money. It’s better to spend it on a well-designed dendroplane!
The cutting down or replanting of green spaces on the territory allocated for development is determined by legislative norms for environmental protection. In accordance with the rules for carrying out work, the developer must obtain a special permit - a logging ticket, in the presence of bushes and trees that are subject to destruction or replanting. This requires dendrological research. In this article, we will get acquainted with the composition of these works, and also consider what a dendroplane is (examples of ready-made plans will be given for maximum clarity).
Composition of engineering surveys on dendrology
- Inventory of green spaces, examination of their current condition.
- Estimating the compensation value of trees to be cut down.
- Compiling a list of all green spaces indicating qualitative, species and quantitative characteristics.
- Development of recommendations for cutting down or preserving trees.
- Creation of a dendroplan, accounting sheet and explanatory note.
Important:
The main goal of dendrological research is to minimize harm to nature during the construction or reconstruction of objects, as well as to protect the environment.
An example of a project with working drawings – Photo gallery – “Garden fantasies”
An example of a landscape project for a small garden with working drawings. Such a project usually includes the following sheets: - general plan - layout drawing for the layout - dendrological plan - layout and planting drawing - paving schemes, types of lawn coverings - garden lighting diagram - automatic watering diagram Also included in the project is an assortment list, estimate, structures retaining walls and road surfaces, reservoirs, sketches of 1-2 viewpoints. The composition of a particular project depends on many factors; the number of required sheets can vary both up and down.
SketchSketch | General planGeneral plan | Layout drawing for planningLayout drawing for planning |
Dendrological planDendrological plan | Layout drawingLayout drawing | Lawn coveringsLawn coverings |
PavingPaving | LightingLighting | Automatic watering |
What is a dendroplane?
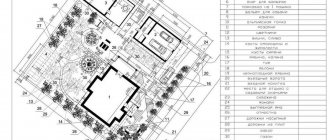
A professional dendroplan allows developers to make cost-effective decisions on the placement of objects on the ground in relation to existing plantings, taking into account state requirements for nature conservation. It is a special topographic map of the site with a detailed indication of the number of green spaces, the perimeter of their location, as well as species and quality characteristics. Each individual shrub, lawn or tree on the dendroplane is assigned a number. Sometimes it can be fractional. In this case, the numerator indicates the number assigned to the plant in the tally sheet, and the denominator indicates the total amount of planting material. The drawing uses symbols. Single plants are displayed as a circle, the diameter of which corresponds to the diameter of the crown of a bush or tree at the required scale. Group plantings are depicted in the form of geometric shapes. As a rule, a scale of 1:500 is used to develop a drawing, but in some cases more detailed detailing may be needed - 1:100 or 1:200, for example, if you need to indicate in detail information about plantings (height, species, diameter). When performing dendrological surveys, special attention is paid to historical, valuable, coniferous, relict trees and shrubs.
The drawing indicates:
- Location of the land plot.
- Ecological, biological characteristics, as well as the characteristics of all plants present on the site of future development.
- Composition and properties of soil.
- Illumination of the area.
- Other data in accordance with customer requirements.
Topographic plan scale and symbols
The dendroplane scale of 1:500 means that five meters of the area on the map are depicted as a centimeter segment. When developing landscape design projects, drawings made on a larger scale (1:100 or 1:200) can be used. This allows you to display each tree and indicate its species, height, as well as trunk diameter.
A dendroplan of a garden plot, made by specialists on a scale of 1:100, with a detailed explanation indicating the names of the plants used in decorating the area
To apply tree and shrub vegetation to the dendroplane, carried out at a scale of 1:500, special symbols are used - circles with a diameter of 3 mm. If the drawing is heavily loaded, then the diameter of the circles is reduced to 2 mm. Following the rules for drawing up a dendroplane, especially valuable trees, coniferous, historical and relict, are highlighted with color or an additional circle of larger diameter.
- If the circle is not filled in on the dendroplane, then this tree must be preserved.
- If the circle is half filled in, then the large tree will need to be replanted.
- If the circle is completely filled in, then the tree must be cut down.
Multi-stemmed trees, like single-stemmed ones, are indicated by one circle on the dendrological plan of a garden plot. Groups of shrubs and trees can be presented on the plan in the form of separate circles or in the form of an oval, occupying the same amount of space on the map, taking into account the scale, as on the site. When performing tree surveys, self-seeding and shoots are indicated by an outline, just like shrubs, not forgetting to assign a serial number.
Important! When transferring existing plants in the form of circles onto a topographic plan, an error of one millimeter on the scale of the drawing is allowed. On the ground this is equivalent to half a meter.
Below are several examples of a dendroplan of garden plots, on which construction objects and green spaces listed in the explication are located schematically.
Dendroplan of a suburban area, on which the buildings are marked with numbers in red circles, and the plantings listed in the legend are numbered in black circles
An example of a dendroplane of another summer cottage, the creation of which used different symbols. In particular, the buildings are numbered with Roman numerals
Remember that spruce, firs and yews prefer to grow in the shade, with a sufficient level of humidity and an even thermal regime, devoid of sudden changes in temperature. When planting barberry and cotoneaster, it must be taken into account that these shrubs require a lot of sunlight. Moisture evaporation and constant temperature changes have a beneficial effect on the well-being of these plants.
Features of documentation.
Currently, the accounting sheet and dendroplan are required to be included in the package of project documentation (if there are green spaces on the site). There are many nuances that need to be taken into account when developing this documentation, so it is important to entrust the work to qualified engineers with relevant experience.
Statement of accounting as part of the dendrological plan
Any design documentation (for reconstruction, construction or major repairs) includes a dendrological study of the territory.
The purpose of this work is to study the green spaces growing in the area. Based on the results of the survey, specialists are developing a dendroplane, which allows for an objective assessment of the situation regarding the location of objects, existing shrubs and trees. An addition to the dendrological plan is a tally sheet indicating the amount of vegetation. It contains the most complete information about all green spaces located on the site, including the serial numbers of shrubs and trees, as well as their dimensions (height, diameter), and species names. In addition, the accounting statement indicates the current state of the plantings (dry branches, diseases, damage) and the compensation cost of the vegetation. The statement reflects the results of a field survey of the area, which is carried out by dendrologist engineers. The characteristics specified in the documentation may vary depending on the requirements specified by the customer and the goals of the dendrological study.
The accounting statement contains the following data:
- Plant number (according to the dendroplane).
- Name of the plant (in Latin as well as national languages).
- Plant age and diameter.
- Condition at the time of the study.
- Crown projection and type of root system.
- The designer's decision on the need to cut down or replant a bush (tree).
- Other characteristics.
It should be noted that carrying out dendrological surveys involves the creation of a dendroplan (main drawing), a counting (inventory) sheet, as well as an explanatory note, which explains the goals and methodology of the work, and also indicates information about the land plot. Its registration is carried out in accordance with current regulations.
Important:
The dendroplane and tally sheet contain detailed information about the characteristics of each plant. This allows you to determine its compensation value. Only after these works have been completed is it possible to competently compile a list of existing plantings that interfere with the construction of the facility, as well as draw up a plan for planting new vegetation upon completion of construction work.
Properties of green spaces
The landscape design master faces the difficult task of combining plants with each other. The desired beauty does not always correspond to harmony, since plants planted too close can inhibit the growth of neighbors.
When drawing up a dendroplan, you need to take into account many rules . Form plantings, keeping in mind the future image of the site. Each young plant will grow, which means it will take up more space than at the time of planting. There are computer programs that show what any tree will look like in a year or five years. This provides a good opportunity to see the future of your garden and make adjustments to the planting plan.
When planting trees, you need to know in advance the size of the crown and root system. The selection of green spaces is made depending on the seasons of the year and the calculation of climatic conditions. Many plants have different needs for water, sun and shade. It is advisable not to place two types of plants together, which have different temperature conditions and watering needs. It is advisable to plant heat-loving species with their own kind, sending them to the sun, while delicate species are best hidden in the shade of the house.
If you add calculations of the sun's movement to the plan, you can determine the places where the shadow is cast the longest. It must be remembered that a young tree does not create as much shade as it will provide in the future. If it covers a significant space, many plants will grow worse in its shade.
Green spaces need to be able to be combined with each other, because each tree or bush has a different effect on the living creatures around it. Properly combined plants help each other develop. Plant compatibility has its own rules. To identify a professional among landscape designers, you can ask him questions about compatibility. A master who has studied this issue deeply is able to warn about poor compatibility of planned plantings.
Knowledge of the biological symbiosis of plants allows you to create a favorable microclimate for plants due to the location of friendly neighbors. Some species are frost-hardy, while others love warmth. It must be remembered that exotic plants may not take root in a temperate climate, so you will have to abandon many species from the plant catalog for your dendroplane.
The design rules provide for the placement of paths in order to have convenient access to each type of planting. Paths are designated by one color, most often gray or pink. Asphalt areas are distinguished by their color. When planning plantings, it is advisable to avoid littering with self-seeding over a large area. Over time, the crowded sector will require more and more effort and attention. Shrubs planted too close not only interfere with each other, but also spoil the appearance. A well-designed graphic design allows you to avoid unnecessary work in the future, when you have to take care of the greenery all year round.
Landscape design professionals are able to draw up a site plan taking into account the flowering of all groups of plants. Masters achieve harmony in the color palette of a blooming garden, ensuring the replacement of fading plants with those that are just blooming. Such complex work may be more expensive. When landscaping your garden, you need to stay within your budget.
Examples of ready-made dendroplanes
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with what a dendroplane looks like. (Examples of ready-made plans are given below).
What documents are required to create a dendroplane?
When submitting an application for registration and approval of a dendroplane and a balance sheet by highly qualified specialists of the Hektar Group company, we recommend that you make sure that you have the necessary package of documents.
To create a dendroplane you need:
- Situational plan of the area on a scale of 1:2000 indicating the boundaries of the land plot.
- Geobase (in digital modern format).
- Permits for work.
Assortment list
There is also an integral and mandatory document when drawing up a dendrological plan for a personal plot, it is called an assortment list. The range of plants most suitable for your site should be indicated here. In addition, it allows you to correctly draw up project estimates. When filling out the assortment list, the specialist distributes all types of plants into groups with a clear sequence.
At the very beginning of the list are conifers and shrubs. Next are fruit-bearing trees and bushes. And only after this the larches are brought in, and at the very end - the lianas.
The assortment list must include the full names of plants (including in Latin), and also indicate the number of copies of each species required for planting. Also, the document must reflect all the characteristics of each plant, such as height, species characteristics, type of roots, etc.
In what cases is dendrological research required?
A dendrological plan is necessary when carrying out restoration, construction or repair work, if it is planned to transplant or cut down trees (shrubs) on the site. In this case, you need to obtain a logging ticket and a conclusion from the regulatory authority (Department of Natural Resources). Only if these documents are available, the developer has the right to replant or cut down green spaces. If plants are destroyed or damaged during the work, the developer must fully compensate for their cost and carry out landscaping of the area upon completion of construction in order to compensate for the damage caused. A dendroplane is also necessary when designing landscape design for a visual representation of the composition. In addition, it is required to carry out work on landscaping the land.
A dendrological plan is an obligatory component of competent landscaping of a land plot, regardless of its intended purpose. The creation of gardens and park areas, as well as the harmonious distribution of shrubs and trees, is essential for urban planning. Also, these events are an important element of urban ecology.
A dendroplane is required in the following situations:
- To carry out construction or restoration work in areas with green spaces.
- To carry out landscaping work.
- When designing landscape design.
Rules for compiling an assortment list
When planning plantings on a garden plot, an assortment sheet is attached to the dendroplane, which lists all purchased plants. This document allows you to draw up a project budget, justifying all cost items for the purchase of the necessary planting material. When filling out the assortment list, plants are placed into groups in a certain sequence. Coniferous trees and shrubs are indicated at the beginning of the list. Then comes the turn. Then all the leafy plants are brought in, and after them - the vines.
The assortment list must indicate the full name of the plant, including in Latin, and the required number of planting specimens. In addition, the assortment list reflects the characteristics of plants, such as height, crown projection, decorative features, type of root system, etc.
The preservation of tree and shrub vegetation during the construction of objects is possible with a competent study of the site and the preparation of a dendroplan with a transfer sheet
In conclusion, we can say that a dendroplan, developed by professionals taking into account the requirements for this type of document, allows for the optimal placement of objects under construction, while preserving the trees and shrubs growing on the site. This will affect the reduction of financial costs required when organizing the cutting down of plants and subsequent work on compensatory landscaping. Tree survey provides a rational approach to landscaping, which preserves healthy woody vegetation in its virgin form. This increases the attractiveness of the site and reduces (or completely eliminates) the purchase, delivery and planting of large trees.
The dendroplan of the site occupies one of the most important places among all the project documentation attached to it. A dendrological plan is a drawing on which all the plants planted in a garden plot are marked.
When creating such a plan, a careful selection of plants is carried out that will be fully compatible with the overall design style of the garden plot, as well as with each other, depending on the biological characteristics.
In addition to plants, the dendroplan includes images of various buildings, which include paths, planned extensions, boundaries and zones.
An example of a dendrological plan for a garden plot
Thanks to the creation of a dendroplane, many important points can be taken into account in a timely manner: the characteristics of the garden plot, the ecological and biological characteristics of plants, and much more. Perhaps the main feature of the plan is to recreate the maximum size of plants (in adulthood), which must be taken into account during planting.
An example of a dendroplane of a garden plot with a gazebo and a hedge (the sizes of plants are indicated in their adult form)
Drawing up a dendroplane, of course, cannot be done without a professional specialist. All planting places, as a rule, are designated by a fraction, the numerator of which is the serial number of the plant in accordance with the assortment activity, and the denominator is the number of plants of a certain type (if the plant is single, then the denominator is missing).
A dendrological plan is necessary if replanting or cutting down trees is planned during repair and construction work. Subsequently, the dendroplan and accounting statement are submitted to the Department of Natural Resources. The conclusion and the felling ticket, which must be issued by the Department, are the necessary documents that give the right to replant or cut down green spaces. If damage or destruction of plants occurs during the work, the developer must pay their cost, as well as carry out landscaping to compensate for the damage caused.
Passing the state examination
Some of the most important natural resources are trees and shrubs. They perform the function of environmental elements that influence the state of the ecology.
Dendrological examination is a tool that allows you to determine the current state of green spaces and the nature of their damage. It is in the interests of forestry and cities to preserve the maximum number of growing specimens.
Based on the results of dendrological research, the Mosgosstroynadzor (State Construction Supervision) Committee is obliged to provide a conclusion to continue the development of the project. For this purpose, the compiled dendroplan undergoes state examination. This is a mandatory procedure, since it is extremely important that construction is not carried out to the detriment of nature. After studying the project, Mosgosstroynadzor makes a decision on the legal replanting or cutting down of plantings. Conducting dendrological surveys is regulated by the following regulatory documents:
- GOST R 55935-2013,
- GOST R 55528-2013,
- Law of Moscow dated 05.05.1999 No. 17.
It should be taken into account that this document is valid for 4 years from the date of examination by the regulatory authorities. After this period, repeated research is required. When updating the dendroplane, a mandatory reconciliation with the reconciliation sheet is carried out.
Main types
There are two types of dendrological plans, the difference of which is determined by the type of work to be done:
- Compensatory or future landscaping plan;
- Plan of existing plantings.
The first is compiled after cutting down existing vegetation to compensate for lost landscaping. The same type of documentation is used if there is no vegetation on your dacha property that would interfere with the planned construction and does not require relocation or destruction. You can limit yourself to the choice of fruit trees, shrubs and ornamental plants for your local area. In this situation, the dendroplane will not require calculation of compensation payments for damage caused to nature. You won't face any fines either.
The second is carried out if it is necessary to clear a future construction site from interfering trees, bushes, and dead wood.