Natural bodies of water: lakes
A lake is a part of the earth’s water shell, formed in depressions of various origins. Lakes are salt and fresh water bodies. They are studied by the science of limnology, which claims that they are not part of the World Ocean. Often these bodies of water are salty. This is due to the fact that the process of accumulation of minerals occurs in them. The reason is the low level of runoff and water exchange. Bottom sediments accumulate at the bottom of lakes.
The main classification is based on the shape and origin of the basins. The most common of them are tectonic, formed in faults in the earth's crust. Lakes of the volcanic type are formed in the craters of extinct volcanoes, mainly in the mountains. Zaprudnye are formed in places where a fragment of a mountain blocked the path of a river. Due to the dissolution of rocks, karst lakes are formed. In the mountainous regions of the Alps, the Caucasus, and the Urals, glacial reservoirs form. These lakes are formed by glacier activity.
Classification according to various criteria
There are the following types of reservoirs:
- Pond.
- Lake.
- Old lady.
- Reservoir.
- Sea.
- Ocean.
Physical, chemical and biological processes occur differently in different types of reservoirs.
Based on their origin, reservoirs are divided into natural and artificial . Natural bodies of water are natural ponds and lakes. Artificial ones are divided into three main groups:
- Reservoirs (water volume more than 1 million m³);
- Ponds (water volume less than 1 million m³).
- Pools completely isolated from the external environment and with full regulation of the water regime.
Artificial reservoirs also include excavated quarries and dams.
Reservoirs can also be permanent or temporary. The latter occur only during periods of high water. These include oxbow lakes and puddles that form in the spring when large rivers flood. Based on their chemical composition and the amount of salt in the water, water bodies are divided into salty and fresh. It is also worth considering a more extensive classification of reservoirs.
Constructive separation
Quite often, ponds are created at landscape architecture sites, which are classified according to design characteristics into the following types:
- Small and ultra-small reservoirs. They are characterized by ready-made lining of the bottom and sides, produced in a factory (film or a ready-made bath). They can be considered swimming pools, because they are completely isolated from the environment and are filled artificially. A feature of such pools is the need for drainage of the area where they are located. Failure to comply with this rule threatens to “raise” such a reservoir above the surface of the earth, which leads to a violation of the aesthetic properties of the object.
- Dam reservoirs. They are erected on permanent and temporary watercourses. Their main purpose is to regulate channel flow, which is especially active in the spring. Thanks to the regulation of flow for economic purposes, it becomes possible to use water for watering plants in the summer, as well as to create full-flow reservoirs. As a rule, their volumes range from hundreds to millions of cubic meters of water.
- Dug. Created by excavating a pit in the ground and then filling it with water. The shapes and sizes of such reservoirs vary from tens to tens of thousands of cubic meters of water with an average depth of 1-2 m. Usually their sizes are much smaller than dams, because their creation is a very labor-intensive process. To make sure how labor-intensive it is, for clarity, they use an indicator such as the ratio of the volume of accumulated water to the volume of excavation work performed . Ke is the efficiency coefficient of the reservoir device. For dam reservoirs it usually ranges from 20 to 100 or more, while for digging ponds it is almost always less than one.
- Combined. In the process of their creation, various techniques and design solutions are used. For example, a dam reservoir is created, which takes shape as close as possible to natural ones. This leads to the fact that in the upper part the object becomes narrow, approaching the width of the stream bed. You can also give the outline an artificial shape if necessary.
Purpose of water bodies
Based on their main purpose, water bodies are divided into several types:
- Decorative. These usually include small and ultra-small reservoirs. Their livelihoods are entirely carried out at the expense of humans.
- Landscape and decorative purposes. They act as an important part of the planning structure of the facility. The water exchange coefficient (the ratio of the volume of water passing through a reservoir during the year to the amount of water contained in it) is usually from 2 to 2.5. At the same time, economic use of water is not provided.
- Recreational. The difference from landscape and decorative ones is the recreational (restorative, health-improving) load. In addition, the requirements for water purity are quite high. They have a high water exchange coefficient of 2.5−3. Near such reservoirs, buildings for domestic purposes to meet the needs of vacationers. The volume of these water bodies must be quite large. This will reduce the level of water pollution and improve the natural flow of biological processes.
- For water sports: they are designed and built in accordance with the necessary standards. It is also important to comply with all regulatory parameters during their construction. Aquatic vegetation is usually excluded. Sports facilities are being built around the reservoir in order to use the facility for its main purpose.
- For sport fishing. There are two types of reservoirs: small ones for individual use, and larger ones for collective use. Large fish are usually released into small bodies of water, and the water exchange coefficient in them should be 4-5. Fish are not left for the winter. Large fishing reservoirs are characterized by the presence of wintering pits (3-4 m deep) for wintering fish. Stocking is carried out with different fish, regardless of its size. During sport fishing, average feeding of the fish is carried out. During the period prohibited for fishing, intensive feeding is carried out in order to accelerate their growth and weight gain.
- Fish farming for economic purposes. It is desirable to have surface runoff water that is warmer and rich in oxygen. In underground waters, fish develop twice as slowly. Fertilizing causes water pollution, as a result of which 4-5 times water exchange is necessary. A wintering pit is required. A special feature of these reservoirs is the presence of a cage with lattice walls for catching fish. This process occurs due to the release of water into the cage. Then, when the bulk of the water has been dumped, the fish are scooped out with a net.
- For irrigation of the territory of the facility . The creation of such reservoirs is aimed at accumulating and further warming water, which is used for irrigation. This is of particular importance if such a site is filled with cold, low-oxygen groundwater. The water must be clean to avoid clogging the devices. Water exchange must be carried out about 3-5 times.
- Multifunctional. Quite often there are cases when an object performs several functions simultaneously. In such situations, the requirements for it depend on its specific purpose.
What is a pond?
A pond is a body of water of natural or artificial origin. It is created for the purpose of conserving water, irrigating surrounding areas, and breeding fish. The natural pond is a small lake.
An artificial pond often serves as a reservoir. They form it by blocking the path of the river and forming a dam. The artificial pond is fed mainly by groundwater or river flow.
Ponds are fresh water bodies. To simplify the drainage of excess water, artificial drains are formed. Ponds are often found in rural areas. Here they have a certain economic role - raising fish, storing water for irrigation, and sometimes doing laundry.
There are two types of ponds: dug and dam. The inhabitants of reservoirs are protozoa, algae, and fish. Special ponds are created for breeding valuable species of fish - trout, sturgeon, stellate sturgeon. Reservoirs are specially cleaned and their own ecosystem is formed.
What types of artificial reservoirs are there?
Artificial reservoirs are:
- Reservoirs. They can be of large volume, dams - erected on watercourses and designed to regulate channel flow. They are filled mainly due to surface water runoff. There are also dug reservoirs, when a pit is dug in the ground and artificially filled with water. Their sizes are much smaller than those of dam reservoirs.
- Ponds. These are the same reservoirs, but only with a smaller volume of water. Depending on the method of creation, they can be fed by river flow, groundwater, or completely artificially filled.
- Swimming pools. These are small-volume ponds with a lined bottom and sides, the water regime of which is completely regulated by humans.
The listed reservoirs are permanent, but there are also temporary ones. They arise as a result of floods of large rivers and are called oxbow lakes.
Thus, we have come to the conclusion that our favorite country ponds and fountains are also reservoirs created artificially. Most often, the purpose of their creation is decorative decoration of the site. But, if you wish, you can always create an entire ecosystem in the ponds by populating them with fish and planting plants.
Video about what types of reservoirs there are
Reservoirs are natural or artificial accumulations of water that can be permanent or temporary in nature, decorative, and located in parks and gardens. The flow of reservoirs is slow or absent.
The importance of reservoirs
Reservoirs are artificial reservoirs formed to store water on an industrial scale. There are channel and lake reservoirs, depending on their origin. They can also be covered, open or dammed.
The world's largest reservoirs: Bratsk, Rybinsk - in Russia, Smallwood - in Canada, Nasser - in Egypt and Sudan. The creation of such reservoirs has enormous consequences, but not always positive ones. The main one is a radical change in the landscape. This applies to both fauna and flora. They have a negative impact on fish spawning conditions.
Not the best consequence of the creation of such reservoirs is the siltation of reservoirs. The process represents the formation of large sediments at the bottom. The water level decreases. This process has been studied in detail because it harms the ecosystem. The inhabitants of reservoirs may change.
Where do oxbows come from?
Oxbow lakes as natural reservoirs are part of the channel where a river previously flowed. Another name is old speech. Such reservoirs often have a bizarre shape - a sickle or crescent, a loop, a curl. How are oxbow lakes formed? The formation process occurs when, for some reason, the channel straightens, and the previous curl or curvature remains cut off from the main body of water. The main reason is high water, when the river finds a more convenient path.
Sometimes the bends of one river unite - this is how oxbow lakes can also form. This process occurs when there are a large number of sleeves. The entrances to the oxbow lake are gradually covered with silt, and the reservoir itself turns into a lake or swamp. If there is food, it can function, but if not, it can dry out. The largest oxbow lakes can be more than 500 meters long.
What do reservoirs feed on?
The type of nutrition is one of the main characteristics of a reservoir. It can characterize its structure and functions.
How can bodies of water feed? Firstly, external surface runoff - rain, other hydro objects. Secondly, groundwater, which can come close to the surface. Thirdly, artificially - the basin of the reservoir is filled forcibly. Fourthly, replenishment with combined type waters.
Drinking groundwater is the most environmentally friendly because it is clean. If the lake has such nutrition, then duckweed and mud will form in it less often. The most common type of nutrition is combined.
A guarantee of constant filling with water is the forced implementation of this process. Fill the reservoir with either tap or irrigation water. The most common diet is a combination diet. Its sources can be rain, melted snow, groundwater and much more.
Flora [edit | edit code]
The plants of the reservoir are varied in shape [3]. Reeds, cattails and reeds [4], hornwort, sedge, calamus, duckweed, bladderwort, susak, egg capsule [5] and others grow in fresh water bodies. Rice loves moisture very much, and its shoots grow directly from the water [6]. More than 30 thousand species of algae grow in salty reservoirs [7].
- Author: Maria Sukhorukikh
Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(8 votes, average: 2.3 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Reservoirs and their location on the ground
Reservoirs are hydraulic objects located in a certain area. Where can they form? The place of formation, for example, of a lake, can be a river bed. The reservoir can be dammed or dug. Power is supplied, as a rule, from the river. Slope, watershed, and floodplain reservoirs are formed on the relief. In such cases, the relief of the lake or pond is clearly visible.
In the floodplain, reservoirs with underground, combined, and channel feeding are formed. They can form in an oxbow where sluices are installed. A dam and pumps can also be located here to use such a reservoir in industry.
Slope reservoirs are formed on the terraces of river valleys. They differ from others only in some design features.
Watershed reservoirs are constructed in watershed areas. They can feed on groundwater or artificially. Water can be forcibly supplied from a river or well.
There are also reservoirs in embankments or excavations. They are quite widespread, they are easy to form and organize their nutrition. They can have any area. They are quite expensive to build.
In embankments, reservoirs serve primarily to store water. Such an object could become the basis for a hydroelectric power station.
What are the names of the bodies of water that nature created?
The sea, ocean, lake are natural bodies of water, they were created by nature. Man also creates bodies of water: ponds, reservoirs. They are called artificial reservoirs.
Interesting materials:
How to find out how many times you have watched a video on YouTube? How can I find out how many bits my system has? How to check battery status on iPhone 5S? How can you tell if mussels are fresh or not? How to find out your CVV code of Kaspi? How to find out your YouTube ID? How to find out your Yardpou code? How to find out your personal account on MTS? How to find out your account on a laptop? How to find out your property tax debt?
Creating a decorative pond
Decorative pond - what is it? This is an artificial water body that serves as a decoration for the site, creating its complete appearance. Most often, owners of private houses and summer cottages come up with the idea of creating a decorative pond.
Artificial ponds are beautiful and stylish. What do you need to know to successfully create such a site decoration?
Creating a pond with your own hands is a feasible task for everyone. The shape and design of such a cozy corner of the garden can be very diverse. An artificial pond will fit perfectly into any landscape and can become its structural dominant.
To begin, choose a place that is not very close to your home (it is better to consult with landscape design specialists). Close proximity to the house can harm the foundation.
You need to create a project. To do this, determine the shape of the reservoir: oval, rectangle or intricate figure. The project will allow you to determine costs, materials, and location of filtration systems. Next, you should choose high-quality materials - the durability and beauty of the pond depend on them.
When everything is selected and purchased, proceed. Preferably, not on your own, but with the help of qualified specialists. The final stage is decoration with plants. This will complete the image of an ideal pond. You will get a gorgeous pond - the photo below represents one of the possible options for your garden.
Further care of the pond
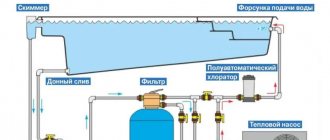
An important condition for keeping a reservoir in perfect condition is regular maintenance. If the structure is properly created and the correct location is chosen, you will not have to devote much time to the reservoir.
But no one is immune from various situations - pollution, blooms and lack of oxygen. Problems can be solved by removing excess algae with a pitchfork and rake, and using a filter will also help. Chemicals are recommended for use only if they cannot harm growing and living things. The appearance of silt or darkening of the water signals the need to change the water. To enrich water with oxygen, you will need to purchase and install one of the types of aerators.
The foundation and maintenance of the reservoir must be approached carefully. In order for it to always please the owners and guests, you must first choose the right place for it, decide on the shape, size and variety, carry out work on its design, and also monitor its condition.