- Lighting requirements
Raspberries have long been firmly established in many household plots, providing gardeners with tasty and healthy fruits. This crop thrives in regions with a temperate climate and is relatively unpretentious, but in order to get a good harvest, you need to know at what distance to plant raspberries and how to choose the right planting material. This will be discussed in the article.
Large-fruited and remontant varieties are of increased interest among summer residents.
Outdoor cultivation technology, care features
Planting and growing raspberries is very simple. The crop is able to grow and bear fruit, even if you take care of it in a minimal amount. The key elements to successfully growing raspberries are:
- careful selection of varietal material;
- site selection;
- method of caring for shrubs.
If everything is done correctly, you will be provided with a stable harvest for 10 years. When choosing from classic and remontant varieties, purchase the latter.
- They have a number of advantages:
- fruiting - 2 times a year;
- The life cycle of the main crop pests coincides with the stages of the growing season of classic varieties, and remontant varieties bloom a week later, so they are almost not attacked by harmful insects.
Most varieties are intended for cultivation in frost hardiness zones 3–10. The third zone includes the Urals and Eastern Siberia with minimum winter temperatures down to -40°C, the fourth - the Moscow region (-35°C), and the ninth - the Black Sea coast of Crimea (-7°C). All you have to do is choose the variety that can be cultivated in your climate zone. Also pay attention to the degree of protection of plants from diseases. The colder the region is in winter, the higher it should be.
Did you know? The ancient Greeks first discovered raspberry bushes on Mount Ida. This is where the Greek name for the plant comes from
-
"Ideus".
Raspberries reproduce by shoots that form on the creeping root system. Therefore, the area for it should be quite spacious. By planting just a couple of shoots this year, you will get up to 7 new ones next year (in the same place). Maintain a distance of about 1 m between rows, the width of which should correspond to the size of the shrubs.
The plant “hates” wetlands and stagnant moisture at the roots . If you have clayey soil that does not drain well, make a high bed. This is a structure that is raised to a height of 20–30 cm above the ground. It is convenient in areas where long rains begin in the fall, which can cause the roots to become wet.
The bed is made in the form of a box made of wood, plastic, metal, or other material and filled with a soil mixture of the following composition:
- 3/5 of leaf soil (top layer of garden soil);
- 1/5 part sand;
- 1/5 part of peat or rotted manure.
Raspberries prefer neutral soils with an acidity level of about 6.0 pH. If the soil is acidic, then prepare the bed six months before planting by adding slaked lime (300 g/m²). Do not plant bushes where tomatoes, peppers or potatoes previously grew. Fungi that infect these plants can also destroy raspberries.
Where can I plant
When determining where it is best to plant raspberries, you need to consider several main factors.
Illumination
Raspberries need sunlight. It does not tolerate competitors and grows and bears fruit well in a well-lit place. If there is not enough sun, the shoots grow, and the berries become smaller, they become smaller and lose their sweetness.
The soil
Not being picky about the composition of the soil, raspberries will feel at ease in any area, but the seedlings have a special affinity for loam and black soil. It is recommended to add wood ash to acidic soils.
Wind protection
To prevent raspberry bushes from breaking under gusts of wind or during a thunderstorm, they are planted along the fence or in the garden.
Humidity
Raspberries do not like lowlands or steep slopes, since with such planting there is a risk of moisture stagnation, and excess dampness is harmful to the roots and has a bad effect on the taste of the berries. For the same reason, the proximity of groundwater is undesirable.
Variety selection
Red raspberries are widespread in all regions of Europe, Asia and North America. But besides this, there are many varieties with yellow, black, white and purple berries. They bear fruit well and interbreed with each other. Therefore, it is not recommended to plant varieties with dark and light fruits next to each other. Between such plants make a distance of at least 3 m.
The work of modern breeders is aimed at obtaining plant species that are as resistant to diseases and cold climates as possible . North American varieties have thinner shoots. They are better adapted to northern conditions than European ones. Black raspberries are usually of American origin. It is less frost-resistant than red, but is excellent for growing in central Russia.
According to the method of fruiting, classic and remontant varieties are distinguished. The former produce one harvest per year - in the summer. The latter are bicyclic and bear fruit twice. In the summer, the harvest is produced by shoots of the second year of growth, and closer to autumn - by those that appeared in the spring of the current year.
According to the ripening period, they are distinguished:
- early;
- average;
- late varieties.
But there is no clear limit on the number of days it takes for the crop to ripen. Therefore, an additional scale arose: mid-early and mid-late. These are varieties that cannot be clearly fit into one of the groups.
Raspberry varieties with photos and descriptions
Many varieties of raspberries are divided into large-fruited, traditional and remontant. Traditional varieties are distinguished by their reliability, they quickly adapt to climatic conditions and are undemanding to the soil, but it will not be possible to reap a rich harvest from them. The stems of large-fruited varieties branch relatively strongly, due to which they are distinguished by high productivity, their fruits are large and fragrant. Remontant varieties produce 2 harvests per season, and they stop bearing fruit only with the onset of very severe frosts. Also, these varieties differ from each other in the color and quality of taste of the fruit, ripening period, and also in the degree of resistance to diseases and harmful insects.
Early ripening varieties
- Cascade . A medium-sized variety that reacts negatively to drought and is susceptible to blight. The height of the slightly thorny bush reaches 200 cm. The shape of the dark red fruits is blunt-conical, they weigh about 3.5 g, the taste is sweet and sour.
- Cumberland . The variety has moderate frost resistance and resistance to pests and diseases. Black fruits weigh about 2 g. The bush can reach 200 cm in height, the stems are arched, and does not produce root shoots.
- Golden Giant . This large-fruited variety is frost-resistant and has high yields. The large yellow fruits weigh 8–14 grams.
- Vega . The frost-resistant variety is resistant to fungal diseases. The height of the bush is about 250 cm; many small thorny shoots grow. The shape of raspberry fruits is blunt-conical, weighs about 4 grams, and tastes sweet and sour.
- Glen Ampl . The variety was created in England. It is resistant to frost, diseases and pests, and has a very high yield (up to 15 tons of berries are harvested from 1 hectare). The height of the strong bush is about 350 cm, the stems branch well. The rich red, dense fruits have a round-conical shape and weigh about 4 grams.
Late ripening varieties
- Ruby . The frost-resistant variety is susceptible to anthracnose. The height of the plant is about 1.8 m; on the surface of the shoots there are many short thorns of a dark purple color. The shape of the rich red fruits is blunt-conical, they weigh about 3.5 grams.
- Mirage . The variety is resistant to pests and diseases. On the surface of medium-sized bushes there are small, short and fairly soft thorns of a dark red color. The large red fruits have an elongated shape and weigh about 6 grams.
- Stolichnaya . The variety is resistant to diseases and frost, and is distinguished by its yield (up to 4 kilograms of fragrant fruits are harvested from 1 bush). The height of the erect compact bush is about 200 centimeters. The large red fruits weigh about 8 grams.
Remontant varieties
- Orange Miracle . The variety is resistant to pests and fungal diseases. The orange glossy fruits have high taste, they have an elongated shape and weigh from 7 to 9 grams. The taste of the berries is sweet and sour.
- Apricot . The fruits are golden in color with a delicate aroma. Their shape is blunt-conical, and they weigh about 3.5 grams.
- Mulatto . The variety is high-yielding and highly resistant to fungal diseases and pests. Sweet and sour round glossy fruits, dark cherry in color, weigh about 4 grams.
- Diamond . The variety is characterized by high productivity; about 3 kg of fruits are collected from 1 bush. The large ruby-colored fruits have a bright shine and a conical shape, weigh about 7 g. The taste is sweet and sour, dessert.
80.Raspberry. High-yielding raspberry varieties.
Planting in open ground in autumn and spring
Plants are sold from the nursery with “dry roots”. Be sure to soak the rhizome in a growth stimulator for 6 hours before planting. The drug must contain vitamin B1. This will contribute to better development of the root system, and will also have a positive effect on the development of the plant as a whole. Before planting, store the seedlings in a cool place. But it will be correct if you plant the plants on the day of purchase.
We advise you to learn more about the proper storage of raspberry seedlings until spring at home.
Methods for planting raspberries
Raspberries are formed in two ways:
- bush;
- tape.
The first one is convenient if you have only a few bushes. When planting several dozen plants, it is more convenient to place them in rows. Lay rows in the north-south direction. This improves the degree of illumination of each individual shoot.
Deadlines
The optimal time for planting is early spring. Although you can plant bushes in the summer. However, spring plants grow better and bear fruit more actively the following year.
Choosing a suitable location
Select a sunny site with well-drained soil. It should not be located in a low area where moisture and cold air can stagnate. Experienced gardeners advise choosing a site so that the plants are protected from the wind from the north. This could be a fence, hedge, building wall or trees. The minimum distance between the protective cordon and a row of bushes is left at least 50 cm . The slope of the site should be small or absent at all so that moisture reaches all plants evenly. The groundwater level is lower than 1.5 m from the surface.
Be sure to remove weeds. Dig the soil to a depth of 30 cm and remove stones and sticks from it. Break up large clods of earth
Buy manure. If it is fresh, then it must rest for at least 6 months before applying. To avoid burning the roots, when planting, use only stale, rotted manure or bird droppings. Application rate: 4 kg/m². If you use industrial fertilizers, then for planting you will need a mixture of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium with a percentage ratio of parts: 4-20-20. Also prepare material for mulching. This can be straw, sawdust, wood chips, pine needles, film materials.
Important! Raspberries have antipyretic and diaphoretic properties. Therefore, do not use it before going outside in the heat, so as not to increase sweating.
Step-by-step planting instructions:
- Dig holes about 30 cm deep and wide. Plant plants at a distance of 0.8–1.0 m from each other.
- Place a portion of manure or other fertilizer mixed into the soil into each hole.
- Pour in 0.5 buckets of water.
- Place the seedling in the center, straightening the roots.
- Add soil and compact it.
- Cover the root zone with mulch.
Selection and preparation of planting material
A good harvest also depends on the quality of planting material. The seedling is a strong trunk with a powerful root system. Trunk diameter - about 1 cm. Height - at least 40 cm. Root ball diameter - about 15 cm. The trunk must be smooth, straight, without damage. The roots are free of growths and signs of rot (if you cut the root, it should be white).
Selection and preparation of seedlings
Having decided on the varieties, you can purchase seedlings and plant them in pre-prepared areas in the garden. For planting, annual and green shoots are usually used, as well as root and green cuttings.
If you want to propagate raspberries already grown on your site, many gardeners prepare planting material themselves
The table shows the characteristics of the seedlings:
| Type of seedling | Description |
| One-year-old lignified offspring | An annual plant with a rhizome on which there is a developed bud |
| Green Scion | A young plant 20-25 cm high with leaves and an etiolated (colorless or slightly colored) rhizome on which there are adventitious roots, as well as with a part of the mother root 5-8 cm long |
| Root cutting | Part of the root with a diameter of about 1 cm and a length of 8 to 12 cm |
| Green cuttings | Young shoot 5-10 cm high with 5-7 leaves, cut approximately 5 cm below soil level |
It is recommended to buy planting material from the nearest nurseries - this guarantees that you will receive plants of the desired variety, not infected with diseases and pests and adapted to local climatic conditions.
Seedlings must be transported in packaging that protects the roots from drying out.
How to properly care for raspberries, seasonal features
Plant care consists of:
- regular watering;
- application of fertilizers;
- disease prevention;
- pruning of fruit-bearing shoots.
Watering, fertilizing
Raspberries definitely need irrigation. This will allow the farmer to get larger berries and a higher yield. The amount of water required depends on the soil type and climate of the region. The desired irrigation system is drip . It's pretty easy to install. It will save water consumption. In addition, water will not get on the leaves or branches, and the absence of moisture on the plants is one of the ways to prevent diseases.
Did you know? Russia is the largest supplier of raspberries in the world. It produces and supplies to the world market about 125 thousand tons of these wonderful berries per year.
Watering rules in the absence of drip irrigation:
- Water the soil around the base of the bush, not the plant itself. This will prevent rot and disease.
- Saturate the soil with moisture, but do not fill it so that water “stands” on the surface.
- Place a layer of mulch around the base of the shrub to prevent moisture evaporation, weed growth and soil compaction.
- Start watering raspberries in the spring and end in the fall, when the autumn rains begin.
- During the growing season, the most moisture should be given before flowering begins. It is at this moment that a reserve of nutrients for future fruits is laid.
Raspberries grow best in well-drained, fertile soil. Improve drainage and fertility by adding organic matter. This could be manure, compost, bird droppings. They are added before planting. If industrial inorganic fertilizers are used, then take into account that the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium should be the same . For example, 10-10-10 (%). The next year, raspberries are fed at least twice during the growing season: in March and May. The rate of application of inorganic fertilizers per season: 9–10 kg per 100 m² of land.
Find out also how to feed raspberries in the spring for a good harvest.
Plants require significant amounts of nitrogen to grow. But they add it only during March feeding. This could be 100 g of ammonium nitrate applied under each bush. After flowering, nitrogen is not needed. And it is excluded from the composition of fertilizers after flowering, since plants need fruits, not leaves.
Loosening, weed removal
Weeds in the garden aren't just aesthetically bad. They compete with cultivated plants for water and nutrients. If you do not cover the root zone with mulch, you will have to remove weeds every other day. They grow quickly, especially after rain. The depth of soil loosening is up to 10–15 cm. A garden hoe is suitable for this. But you need to use it carefully so as not to damage the bushes. Weeds with tap roots are removed from moist soil by hand, and those with creeping roots are cut with a flat cutter.
Read how to properly mulch raspberries.
Mulch for covering can be straw, wood chips, sawdust, cardboard and other materials . The sawdust layer can be about 3–5 cm thick. During the summer, this layer is periodically renewed by adding a new one, since the lower layer will decompose, enriching the soil with humus.
Pruning in spring and autumn
The main purpose of pruning is to get rid of old shoots, allowing new ones to grow. At the end of summer, shoots of the first year of development begin to bear fruit in the upper part. In early spring they are cut or left for June fruiting in remontant varieties.
We advise you to read about when and how to prune raspberries correctly.
The usual method for pruning raspberries is to simply cut all branches down to about 2-5cm above ground level. But if you prune remontant varieties like this, there will be no harvest at the beginning of summer. Therefore, the shoots on them are reduced to the part that bore fruit at the end of the summer of the previous year. Fruiting in July will occur on them in the central part. And next spring they need to be cut out completely.
Garter
Bushes over 1.5 m in height must be tied up. Raspberry branches are quite fragile; they can break under gusts of wind. Therefore, the trellis performs several functions at the same time. Securely fixed branches will be evenly illuminated by the sun and blown by the wind, which is good for the prevention of diseases , berries will not fall off and they will be convenient to care for and harvest.
It will be useful for you to learn how to care for raspberries in the fall.
Making a trellis . Support pillars are installed along the edges of the row. They are placed in the ground to a depth of about 0.5 m. There should still be about 1.5 m of the column above the soil surface. In long rows, support pillars are placed along the length of the row every meter. A wire is pulled in the middle and at the top of the supports. Use soft pieces of fabric for garters. They should not pinch the trunk so as not to impede its development.
Reviews from gardeners
Ivan: “I’ve been growing raspberries on the plot for a long time, and I specially planted varieties of different ripening periods. It turns out that my raspberries bear fruit all summer, and I collect several harvests per season.”
Alina: “I recently planted bush varieties and was very pleased. The culture is unpretentious and does not require much effort. I do 2 feedings: spring and autumn, pruning, watering and shelter for the winter. The harvest is excellent.”
Kira: “Growing raspberries is not at all difficult, but you need to follow simple rules of care. I feed and water the bushes in a timely manner, tie them to high trellises, and maintain a distance of at least 1.5 m between plants. Pruning and the correct choice of varieties are important.”
5/5 — (1 vote)
When raspberries ripen
Raspberries require heat. Its buds will begin to bloom no earlier than the thermometer begins to show a stable +10°C. In different regions, this temperature is set at different times:
- on the Black Sea coast - in March;
- in the Moscow region, St. Petersburg and most territories of central Russia - in April;
- in the North - no earlier than May.
This becomes the first starting point. Approximately 35–56 days are counted from it until the start of flowering. The specific number of days depends on the variety and type: early ones need 37 days, others need more. It will take about a month for the fruits to ripen.
Did you know? Raspberry medicines effectively treat burns and acne.
How to limit the spread of raspberries
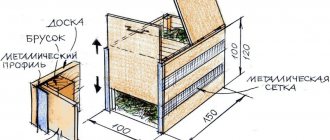
To preserve the decorative appearance of the raspberry tree, a trench 20 cm wide and 30 cm deep is formed along its perimeter, into which a complete enclosing structure is installed. The fence can be made of the following materials:
- slate;
- polyethylene fabric;
- metal or plastic sheets.
Important! To combat overgrowth, the use of fertilizers containing nitrogen is effective.
Alternatively, garlic, sorrel, green beans or corn are planted around the perimeter of the raspberry patch; all these crops limit the spread of the bushes.
How to increase fruiting
Several factors influence the size of the berries and the volume of the harvest:
- water;
- feeding;
- pruning
Raspberries love water . Moisture has a major effect on the size and taste of berries. Water sufficiently every 3-4 days. To better saturate the soil, divide the watering into 2 parts and water it with an interval of 1 hour.
Always try to use organic fertilizers . They are released gradually, providing the plant with nutrition as needed. Raspberries spend a lot of energy on fruiting, so without fertilizing the yield will be significantly lower.
If you want large, juicy and sweet berries, you must provide the plant with water, nutrition and choose the right pruning method for your varieties.
If you cut off branches of the second year on remontant varieties, this also reduces the yield. Although some gardeners note that this increases their yield on the shoots of the first year. It is also necessary to shorten tall varieties. A shoot that stretches up to 2–2.5 m will not increase fruiting, but will reduce it, since a lot of energy will be spent on the development of the shoot itself.
Fertilizer
As mentioned above, raspberries are a perennial plant. It depletes the earth relatively little, but still needs regular feeding. Especially if you have chosen the trench method of planting raspberries, where the bushes are more crowded in a small area.
It is not necessary to use mineral fertilizers - you can get by with organic ones. This is a serious plus - many summer residents do not trust “chemical” fertilizers, which they also have to buy.
In the spring, it is advisable to feed raspberries with an infusion of bird droppings - quail, chicken, duck or any other. One kilogram of litter is diluted in ten liters of water and then left for a week. After this time, the solution is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10 and the bushes are watered with the resulting fertilizer.
Green slurry also gives good results. A kilogram of grass (usually weeds) is filled with 10 liters of water - then follow the scheme described above.
In autumn, it is recommended to use a special complex infusion. A barrel or other suitable container is filled two to three full with a mixture of grass, hay, and tops. 200 grams of wood ash, a glass of vermicompost or manure, 300 grams of sugar or old jam, as well as two crayons (the usual ones they write in schools) are also added here. After this, the barrel is filled to the brim with warm water and left in the sun. Within ten days, the active fermentation process begins. After this time, you can use the mixture for fertilizer. When feeding, a liter of the mixture is diluted in a bucket of water, which is poured onto two or three raspberry bushes.
Reproduction methods
Raspberry roots tend to "spread". Therefore, the main method of plant propagation is by new shoots that grow from overgrown rhizomes in unoccupied areas. It doesn’t really matter how far apart the bushes grow from each other. After some time, the plants will begin to take over the free space. You can weed out shoots that appear in the wrong place or deliberately dig them up and plant them in a row as new plants. This is the most common way to get new bushes.
Find out more about the methods of propagating common raspberries.
But, unfortunately, the rhizome lives no more than 20 years. At the same time, the yield of the resulting shoots decreases over time. To restore it, you need to plant new plants. To do this, cut off a powerful one-year-old shoot, cut it into cuttings, and root them in a mixture of nutrient soil and sand. And then they are planted in a permanent place of growth. Only the site for planting should be chosen differently - due to the depletion of the soil by previous plants and its saturation with insect pests and fungal spores.
Caring for seedlings after planting
Immediately after planting, the stems are cut, leaving a length of 30-40 cm. After this, it is necessary to water the seedlings abundantly and mulch the soil. Peat, humus, straw, grass, crushed bark, and rotted sawdust are used as mulch. You can also cover the planting with an opaque film, while the edges of the film are sprinkled with earth, and a small incision is made above each seedling so that new replacement shoots can grow normally.
For tall varieties, it is advisable to immediately build support structures
In the future, you need to ensure that the soil in the raspberry garden is sufficiently moist, loose and not overgrown with weeds. At first, early vegetable crops (radishes, lettuce) are often planted between young plants, and after 2-3 years, lawn grass is sown, periodically mowed and left on the soil surface as mulch and additional green fertilizer.
Diseases and pests
Disease prevention begins with injury prevention. Bacteria and viruses penetrate plant tissues through them. Damage can occur from chewing leaves by insect pests, wind, or animals. Therefore, it is important to begin disease prevention with pest control.
We advise you to read how to spray raspberries in the spring against pests and diseases.
Main raspberry pests:
- Raspberry beetle dangerous because it damages raspberry flowers and ovaries. It is capable of completely destroying the future harvest. It is not dangerous for remontant varieties, as it lays eggs on classic varieties that bloom a week earlier. But if you find crumbling ovaries, treat the bushes with Karbofos.
- Spider mites can also attack raspberries. They appear if the weather is very hot and dry. Increase the humidity by watering, and the pest will become safe for your plants.
- Aphid - small insects that settle in colonies on leaves and shoots. They, like other sap-sucking insects, can be easily destroyed by spraying the bushes with a solution of insecticidal soap.
Raspberry diseases are affected by insects that carry viruses, weather and growing conditions of the bushes. The presence of weeds, dense conditions and poor air circulation will contribute to the spread of disease. Improper watering increases the likelihood of disease . Waterlogged soil prevents the roots from absorbing nutrients. The root system may rot and the plant will die. Therefore, control the conditions in which raspberries grow. Eliminate deficiencies in agricultural technology, and you will reduce the likelihood of disease occurrence by 50%.
Important! To protect raspberries from pests, plant marigolds between the rows. Most insect pests cannot tolerate the essential oils of pungent-smelling plants.
Signs of the appearance of fungal diseases are spots on the leaves . For prevention and treatment, raspberries are sprayed with copper-based preparations: Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate. For treatment, repeat treatment at intervals of 7 days. Viral diseases cannot be treated. Such bushes are dug up and burned away from the site. Nothing is planted in the place of the dug plant for several years. The exact period will depend on the length of time the pathogen persists in the soil.
Aftercare
In order for the planted bushes to grow and bear fruit, they need proper care:
- regular watering. The soil should not dry out; on average, 10-20 liters of water are poured under each bush twice a month or more often (depending on the weather);
- the soil around the plantings is mulched with sawdust, straw, peat, pine needles, and dry leaves. You can cover it with black film. These measures will save you from weeds;
- inspect bushes for pests and diseases (aphids, spider mites, raspberry beetles), if necessary, carry out urgent treatment with special preparations;
- You can achieve bushiness by pinning young shoots to trellises - supports for bushes;
- the ground around the bushes needs to be loosened and weeds pulled out;
- In the fall, the branches are shortened, and the remontant raspberries are cut at the root. Regular raspberries are also cut out once every two years;
- Before wintering, the soil is thoroughly moistened and then covered with dry leaves.
Raspberry lifespan
In a raspberry bush, the lifespan of shoots and roots is distinguished. The root lives for about 20 years. Escapes - only 2 years. In the first year, the remontant shoot will produce a harvest at the end of summer. The fruits will be placed in the upper part. Next year flowering will occur in the middle part. In the third year, such a shoot may grow, but it will no longer bear fruit. Therefore, after fruiting, these shoots are removed.
After 20 years, the root system and the area where the raspberries grow are depleted. Therefore, gardeners recommend periodically changing the location of growing raspberries.
How to prune
In ordinary varieties of raspberries, all shoots that bear fruit this summer are removed, leaving strong annual branches that will successfully bear fruit next summer.
Remontant raspberries can be pruned in two ways. To get a harvest 2 times in a row, carry out the same pruning as with ordinary bushes. If you need fruits only from young shoots, then the bush is cut out completely.
Branches should be cut flush with the ground.
Growing in a greenhouse all year round
Raspberries are a high-value crop, perfect for year-round cultivation in greenhouses. She is always in demand and loyal to the conditions. The bushes do not require auxiliary lighting and develop well in cool conditions . Greenhouse temperature +21°C is optimal for good development and fruiting of berry bushes. If in doubt, remember that raspberries belong to the same family as roses, and they have long been grown in greenhouses.
Raspberry seedlings can be purchased at a nursery or grown from your own varieties, if there are any on your plot in the open ground. Before planting, clear the soil of weeds. Plan to plant raspberries in early spring . Place the rows moving from north to south so that they do not obscure each other. If you want to use a trellis, you need to install it before planting so as not to damage the plants later. In small greenhouses, planting and growing can take place in large pots.
Use a drip irrigation system . Check the soil weekly to determine moisture content and water if necessary. After three months, begin adding additional fertilizer to the soil.
Find out more about the features of growing raspberries in a greenhouse all year round.
The plant requires full daylight. Therefore, the greenhouse should not be shaded by trees . Raspberries do not require high light levels, but maintenance lighting is needed throughout the winter season. This will enhance growth, flowering and ultimately yield. Increase the winter daylight hours to 16 hours.
Raspberries need 200 hours of winter dormancy to enter the next vegetative cycle . At this time, the temperature should not exceed +4°C. Please take this into account when planning work in the greenhouse. Flowering begins approximately 6 weeks after the bushes awaken and the leaves appear. The fruits will begin to ripen after 10 weeks. The harvest will last about 8 weeks . At this time, the berries will ripen gradually; they need to be harvested once every few days.
Landing technology
Before ordering and bringing seedlings to the site, you need to decide where to plant young raspberries. The choice of location also depends on the method of propagation of bushes.
Raspberries, the garden cultivation of which requires knowledge of how to plant them correctly and what distance should be between the bushes, dictates its own rules.
But besides ready-made seedlings, raspberries can be planted in other ways: cuttings, shoots and even seeds.
Cuttings
If you already have raspberries at your dacha or you have the opportunity to purchase not ready-made seedlings, but only branches cut off in the correct way, you should try to root them and then plant them.
Raspberries are cut at the end of June, choosing elastic, dense shoots. After removing the crown bud (to prevent growth), the shoot is divided into parts so that each cutting has 3-4 buds. The lower cut is oblique; it is placed for a day in a solution of a special agent that stimulates the formation of the root system.
Root the cuttings with a sand-peat mixture under a glass cover. After 2-3 weeks, shoots will appear on the cuttings: the protective cap can be removed.
The seedlings will be ready for planting in open ground next spring.
By shoots
Raspberries readily produce young shoots, with the help of which you can also get new independent plants. A strong young shoot 30-35 cm high is separated from the mother bush along with part of the root, the lower leaves are removed, dug up, being careful not to damage the mother bush, and rooted into a prepared hole (with applied fertilizers, water thoroughly).
The planting is compacted tightly and sprinkled with soil again.
Seeds
Growing raspberry bushes from seeds is a labor-intensive process that does not guarantee results, but you can try propagation this way.
Seeds are collected from well-ripened (or better yet, overripe) berries. The pulp is ground on a sheet of paper, wait until the juice is absorbed and the seeds are collected, after which they are dried on a cloth.
You need to store the seeds in a canvas bag (in the refrigerator), constantly moistening it. Another storage method is in a mixture with wet sand (1:5) in gauze or fabric bags. They are placed in a box with moss and put into the cellar, periodically wetting the sand. Storage temperature +30C.
In spring, prepare containers for planting. Mix garden soil with peat in equal proportions, pour it into a container and plant the seeds to a depth of 2-3 cm.
Place the container with the seeds in a warm, well-lit place and water once every 3-4 days. Every 10 days, seedlings are fed with a urea solution. When the sprouts have 2 leaves, they can be planted in the ground.
A separate hole is dug for each seedling, where fertilizers are applied. Before transplanting, it is necessary to thoroughly moisten the soil in the container with seedlings to make it easier to remove the seedlings. Each one is taken out with a lump of earth and carefully placed in the hole. The earth around is well compacted. If frosts are observed on the soil, then it is worth covering the stems with straw or covering them with film.
Preparing for winter
With the onset of cold weather, you will have to remove fallen leaves from the garden. Most of the larvae spend the winter in the tree trunk zone. Therefore, it is dug up to a depth of 20 cm . Winter thaws can be dangerous for all shrubs. Freezing and thawing cycles in the soil push roots toward the surface and contribute to root damage.
To eliminate this situation, after the soil freezes, it is covered with mulch. It will serve as an insulating layer that will “smooth out” temperature changes in the soil and will maintain a stable temperature level.
In regions with cold winters, it is recommended to remove shoots from the trellis. Then they are bent to the ground and covered with a layer of mulch. They will successfully overwinter under the snow, and in the spring they will be raised onto the trellis again
Preparatory activities
Planting raspberries takes place in stages. First of all, preparatory work is carried out.
Selecting a location
Correctly chosen place and soil preparation determine the successful growth and abundant fruiting of raspberries . An ideal place to plant raspberries should meet the following criteria:
- good sun exposure;
- the presence of slight shade to protect the bushes for several hours a day from the scorching sun;
- absence of drafts and gusty cold winds;
- deep groundwater.
Important! The selected area should not be located in a lowland where water constantly stagnates.
Ideal soil for raspberries should be neutral or slightly acidic, and also meet a number of characteristics:
- fertility;
- excellent moisture and breathability;
- acidity level pH 5.5-6;
- presence of drainage.
Important! Fertile loams and sandy loams are well suited for planting raspberries.
Compatibility with other plants
The condition of plants depends not only on compliance with the rules of planting and care. The crops planted nearby are of great importance, as are the predecessors - plants that grew on the site before the raspberries were planted.
Ideal neighbors for raspberries
- Apple tree - does not cause any harm, creates protection against infection with gray rot.
- Dill, peonies, asters, coriander, basil, garlic - attract pollinating insects, which significantly increases the yield.
Neutral neighbors:
- plum, rowan, pear, honeysuckle, gooseberry;
- tomatoes, pumpkin, cabbage, beans;
- juniper, barberry, roses, lilacs, lilies;
- mint, sage, calendula.
Neighborhood with all of the listed plants does not cause harm to raspberries, but also does not have a positive effect on its growth and development.
Unfavorable neighbors
To avoid mutual harassment, it is not recommended to plant raspberries near the following crops:
- strawberry;
- cherry;
- currant.
Good and bad predecessors
Ideal predecessors for raspberries:
- cereal herbs;
- legumes;
- garlic;
- zucchini;
- cucumbers;
- onion.
Important! The following are considered bad predecessors for raspberries: tomatoes, potatoes and strawberries - due to the susceptibility of these crops to the same diseases.
Planting young seedlings instead of an old raspberry tree is possible no earlier than after 4 years . Otherwise, pests and pathogens will attack young bushes.
Soil preparation
For spring planting of raspberries, the soil is prepared in the fall. The procedure includes several operations:
- digging on a shovel bayonet (25-30 cm);
- destruction of weed roots;
- application of fertilizers - humus and wood ash;
- leveling the soil with a rake.
Before planting in the fall, the soil is dug up using a spade, weeds, stones and other debris are removed from it, and then loosened and leveled with a rake. According to experienced gardeners, preparing the soil for growing raspberries involves following several recommendations:
- preliminary planting and cultivation of green manure;
- applying organic fertilizers to sandy or infertile compounds;
- to reduce acidity levels, use dolomite flour, limestone or wood ash;
- adding sand to clayey soil and clay to sandstone.
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting begins in June for early varieties, in July for middle varieties and in late July or early August for late varieties. The collection duration is about 3 weeks. Pick berries every other day. It is preferable to do this early in the morning, as they will last longer when refrigerated.
Raspberries are very fragile, so picking is carried out in plastic containers with a volume of 200–400 g in order to maintain the shape of the berries and not crush those that will be at the bottom. Store them in a cool place until processed or consumed.
On an industrial scale, mechanized means of picking berries are used. This collection is planned at night so that the fruits are as cool as possible. When planning the mechanization of processes, do not forget that you will need to immediately plant plants with row spacing designed for the passage of a harvester. Also keep in mind that not all varieties are suitable for mechanized harvesting, but only those with lateral fruiting.
Berries cannot be stored for a long time. Their shelf life in the refrigerator does not exceed 1 week. You can eat them fresh, freeze them, or process them into jams or juices for winter consumption.
Growing raspberries can be profitable both outdoors and indoors. Buy varieties that are resistant to diseases, follow basic agrotechnical requirements, and then the yield will be high and stable.
Botanical description
Raspberry is a deciduous subshrub with a height of 1.5 to 2.5 m . The culture has a woody rhizome, around which many adventitious roots are formed. This contributes to the formation of a powerful branched root system.
The shrub is characterized
by erect stems .
Its young grassy shoots are distinguished by their rich green color, as well as their surface covered with a bluish coating and numerous small thorns. Within a year, the stems become brown and woody. At the end of fruiting, they dry out, and in the next season new young shoots appear in their place.
Raspberry leaf blades consist of 3-7 oval parts. Their front surface is distinguished by a dark green color, and the inner surface is whitish due to pubescence.
The racemose inflorescences of the shrub consist of small white flowers. As a rule, they appear in the second year of stem life.
The berry consists of numerous fused segments, which, depending on the variety, can have very different colors: crimson, yellow, burgundy-black, etc.
To date, breeders have developed a large number of raspberry varieties, including remontant varieties that bear fruit twice during one season.
Common mistakes and useful tips
The most common mistakes made by gardeners when growing raspberries include:
- incorrectly chosen variety - when choosing, you should pay attention to new varieties that are much superior to the old ones in their quality characteristics;
- ignoring trellises - planting raspberries in rows and then tying them up can significantly improve the yield;
- narrowed or too wide rows - for full growth, the crop needs sufficient space;
- insufficient watering and fertilizing - lack of moisture and nutrition adversely affects the quantity and quality of berries; to prevent this, it is important to strictly follow the rules of agricultural technology;
- errors during planting - incorrectly chosen time, place, insufficiently prepared soil, illiterate procedure.
Where to buy raspberry seedlings
The best place to buy a seedling is a nursery located in your area. This approach has many advantages:
- there is a very low probability that instead of one variety you will get a completely different one;
- you can be confident in the quality of the seedling: planting material from reputable nurseries is usually healthy and grown according to all the rules;
- Finding a nursery in your area is a guarantee that the plant is adapted to the conditions of your region.
Specialized garden centers have also proven themselves well, but it is undesirable to take planting material from supermarkets and other non-specialized retail outlets. Even if he got there healthy, there is no certainty that the plants were stored in proper conditions.
The best time to buy seedlings is September, when their range is widest. But keep in mind that seedlings purchased in the fall must be immediately planted in the garden.
Where to buy yellow and black raspberry seedlings?
Raspberry seedlings with open root system
Requirements for choosing a landing site
When choosing a site for planting raspberries, it is necessary to take into account that this crop is light-loving and in the shade gives a low yield, however, it does not tolerate heat. It prefers areas with moderate humidity; the root system reacts negatively to excess moisture in the soil; therefore, when planting, it is necessary that groundwater does not come closer than 1.5 meters to the surface of the earth. Otherwise, in winter the root system may freeze.
For growth, flat areas with large accumulation of snow are preferred. This will provide the raspberries with a good winter. You can also plant this crop on gentle slopes facing south and southwest. Excess moisture does not linger here, and there are no cold winds.
The soil is preferably clay-sandy with good permeability to moisture and air, rich in useful minerals. It can grow on sandy soil only if a large amount of organic fertilizer is added to the soil.
The soil should not be acidic. To normalize the acidity level, add lime or ash.
Good predecessors of raspberries are:
- carrot;
- beet;
- radish;
- parsley;
- dill.
Formation of bushes
Tall varieties must be pruned, leaving branches 1.8 to 2 meters high. Low-growing bushes should be pruned at a level of 1.5-1.8 meters.
Stake formation method
It provides for the preservation of bush cultivation with the removal of shoots that have grown between the bushes. The shoots are removed when they grow to 10 cm. Those shoots that remain are tied to a stake at a level of 55 and 170 cm. The upper part is either cut off, leaving a bush 2 meters high, or bent into an arc and tied to a stake at a height of 170 cm.
Narrow fan formation method
The bush is divided into two parts. The stakes are driven in on the right and left sides at a distance of 25 cm from the bush. The divided bush is tied up, moving one side to the right and the other to the left. The height of the tie does not change. Shoots grow in the center of the bush. Side shoots must be cut out.
Arch-stake method
The stakes are located in the center of the bushes. The stems, divided into two sides, are tied as follows: the left stems are taken from the second bush, bent and tied to the stake of the first bush. The right stems should be tilted and tied to the stake of the third bush along with the left shoots of the fourth. And so on until the end of the row. With this method of tying, the lateral shoots should be removed, and a new bush should be formed from the shoots growing in the center.