In the fall, after the harvest and the completion of the main work, life on the plots does not stop - the next stage begins for gardeners. The time has come to prepare trees and shrubs for winter and the upcoming season. A number of activities need to be carried out. This includes feeding, covering plants, and pruning. It is pruning and shaping that will allow ornamental and fruit shrubs to overwinter, and in the spring they will be provided with a lush, beautiful, healthy crown. The procedure is carried out after the sap flow period has ended, the crops have gotten rid of their foliage, but before frost sets in (the temperature at night should not fall below -5 degrees).
Types of shrub pruning
Based on the purpose, pruning is divided into the following groups:
- Sanitary.
- Formative.
- Rejuvenating.
Each has its own characteristics, rules and nuances.
Sanitary – for disease prevention
Autumn sanitary pruning is recommended for absolutely all shrubs and trees, fruit and ornamental. The purpose of this event is to prevent the development of all infectious processes, prevent putrefactive formations, and get rid of old, damaged, broken and dry dead branches. After this procedure, the bushes are better ventilated. The branches turned inside the plant are completely removed; unripe ones are cut off at a distance of about 3 cm from the bud.
Shaping - for a beautiful appearance
Formative pruning in late autumn is practiced only for shrubs that bloom in summer. If you do this in the spring, you won’t get a beautiful decorative shape and full flowering. Such plants bloom on last year's branches that have successfully overwintered. These include:
- Japanese quince;
- forsythia;
- mock orange;
- weigela;
- viburnum-leaved bladderwort;
- lilac;
- action;
- spirea;
- three-lobed and steppe almonds.
Formative pruning allows you to transform a simple shrub into a decorative one. To do this, every year, in addition to the main branches, 2-3 new, strongest shoots are left.
Garden plants with a developed root system require special attention: white snowberry, serviceberry, fieldfare. When forming them, control not only the height, but also the width, cutting off the root shoots along the entire perimeter. In young crops it is also very important to prevent excessive crown growth.
Important! An interesting plant is the mountain ash. Read the article at the link.
On the other hand, you shouldn’t get rid of all the shoots too zealously; this will result in a loose structure and an unsightly appearance of the bush. First of all, old, weak, non-viable branches coming from the roots are cut off. Strong ones are eliminated only in cases where they grow crookedly, towards the bush itself or interfere with the development of young shoots. They leave shoots that can eventually replace old and diseased branches.
In plants that do not tolerate frosty winters well, dried branches must be removed. The cut is made at a distance of 1 cm above the second bud. There will be no need for shoots, branches and shoots that spoil the overall perception of the decorative appearance of the bush.
For bush rejuvenation
Rejuvenating pruning of ornamental shrubs is used to obtain a rich harvest in cases of fruit trees and dense flowering and landscaping for plants that decorate the garden. This method is also suitable for old, poorly growing (less than 6-8 cm per year) crops. The ideal time for the procedure is from August to September.
It is important for novice gardeners to know that pruning is done after flowering. The branches are shortened by 30%, the length is measured from the top. As a result, due to the side shoots, the bush will become more luxuriant, the number of inflorescences will increase, and on fruit bushes the quantity and quality of fruits or berries will increase.
This procedure is carried out every two years. This will allow you to maintain the necessary aeration and decorativeness of the bush.
Scheme for pruning ornamental shrubs according to the rejuvenating type:
Nuances that a gardener needs to know
When performing anti-aging pruning of garden and ornamental crops, you need to take into account some features and consequences. Namely:
- Removing branches, among other benefits, allows you to control the size of the inflorescences. If you greatly shorten the length of the branches, the flowers will become larger, but their number will be significantly reduced.
- If the procedure is carried out regularly, the bush will lose its crown density and its decorative appearance, so shoots intended for removal must be carefully selected.
- No more than 4 buds are cut at a time.
- Branches are radically removed when the plant has significantly degenerated, after 4 years after planting.
- The gardener must know exactly the flowering characteristics of his shrub - whether the buds form on last year’s branches or on fresh growth. Depending on this, old branches or excess growth are cut off.
- In difficult cases, when the bush has stopped producing young shoots, and the old branches are weakened and damaged, a radical rejuvenation procedure is used. Cut off all branches completely at ground level. If the bush was initially formed on a rootstock, pruning is done at a distance of about 15 cm from the grafting. This will activate the growth of fresh shoots, since the base, that is, the root system, will remain the same. After a year or two, the formation of the bush begins again according to the general rules.
Pruning coniferous shrubs
Coniferous shrubs are not pruned regularly. This is justified only in the case of diseased, weak and damaged branches. Another reason is to add a decorative touch to the landscape or use plants as hedges. In order to minimize the traumatic nature of the procedure (conifers are very difficult to tolerate pruning), some features should be taken into account:
- The hardiest type of conifer is the yew. You can form it without fear. All other trees and shrubs must be treated with extreme caution.
- Only the green part is removed; the brown branches should not be touched - they cannot be restored.
- It is important to choose the right tools.
- The safety of the procedure and its effectiveness depend on disinfection.
- No more than 30% of the greenery is removed at a time.
- Cypress and larch trees are pruned in November (the specific time depends on the region).
- The cutting angle for the bud is 45 degrees.
- To preserve the natural appearance, only the internal branches are thinned out.
Some coniferous shrubs lose their attractive, unique coloring with age. Pruning can fix this. For example, the cypress becomes a luxurious plant with a thick, silver-colored crown.
Other garden plants
It is impossible to say exactly when it is better to prune trees, in autumn or spring. In general terms, it can be determined that sanitary pruning is most often carried out in the fall, formative and restorative pruning in the spring, and corrective pruning in the summer. Apple and pear trees can easily tolerate the removal of branches at any time of the year. The rest of the garden inhabitants tolerate the spring procedure more easily. But it all depends on the region in which the pruning is carried out.
As for the not very common garden ones - sea buckthorn, quince, viburnum, mulberry and others, when pruning in autumn it is better not to take risks and remove only what is absolutely necessary.
Necessary tools - types and purpose
“Cutting” is not an easy task and requires the use of well-sharpened garden tools:
- Secateurs. Needed for cutting thin branches up to 2.5 cm in diameter. There are two types of devices - with a curved blade and a straight one. Thick shoots are cut first; the disadvantage is that it is difficult to trim without gaps. The second has a design in which the blade rests against the end of the tool, so there is no need to check for clearance between the blades. The downside is that it is impossible to trim in hard-to-reach places.
- Lopper. Designed for branches with a diameter of 5 cm. Copes well with shoots deep in the leaf crown and other hard-to-reach places. For work at heights there is a rope lopper.
- Saw. Used when eliminating very thick branches.
- Knife. Multifunctional tool. Used for trimming and stripping thin branches, cutting bark, and correcting uneven cuts.
- Garden shears. They help to form a curly crown and hedge.
- Ladder. When choosing it, you should pay attention to stability and widely spaced legs.
Scheme for proper pruning of ornamental shrubs
The main requirement when pruning is to do no harm. To ensure that the procedure goes without consequences, follow the following rules step by step:
- Dried, damaged, old and broken shoots are removed.
- The cuts are made even; there should be no split stumps.
- If a branch is cut without subsequently leaving a stump, then this is done at an angle of 45 degrees.
- All tools used are thoroughly washed and sharpened.
- For branches up to 2 cm, use pruning shears; thick ones are cut with a hacksaw.
- All actions are carefully verified so as not to affect other shoots.
- If you need to stimulate the growth of weak shoots, cut them shorter. To form a decorative appearance of the bush - only the tops.
- The cut must have a smooth surface.
- To avoid pruning, it is better to simply pinch the shoots in time.
After the procedure, the sections are treated with garden varnish; for thick branches (more than 3 cm in diameter), oil-based paint is used.
How to carry out the procedure for hydrangeas?
Gardeners grow hydrangeas to add decorative beauty to the landscape, so this plant needs pruning to increase the intensity of flowering. Adult cultures aged 5 years and older are subjected to the procedure. Old branches are removed at ground level, cutting them off completely. Leave no more than 5 shoots. If everything is done correctly, in the spring young branches will appear, formed from buds on the root collar. The old ones will be renewed and bloom again.
Another way to renew hydrangea is to remove the buds (faded) at a level of about 40 cm from the soil surface. In this case, in the spring there will be a significant increase in fresh, young shoots on last year’s, quite viable, strong branches. They will not break or sag under the weight of inflorescences and flowering caps.
As for the roses.
1. All roses, except climbing and park roses, need to be pruned well to the top level.
2. Be sure to remove fallen leaves so that they do not start to rot. In addition, dangerous pests or mushrooms can hide under them in winter.
3. If there is a need for this, a garter should be performed. Roses should be covered using a dry frame, pre-covered with plastic film or thermal insulation material. Some varieties are enough to be covered with spruce branches.
4. As for climbing roses, they are afraid of the frosty daytime sun, as well as cold night frosts. Therefore, it is advisable to remove such plants from supports and lay them on the ground. Cover the top with spruce branches. For standard roses you will need jute bags or dry leaves. You need to cover the trunks of roses of this type with burlap ribbons.
Proper pruning of berry bushes
The basis of any garden is berry and fruit trees and shrubs. Growing them is not difficult, but it will take a lot of time and effort. Pruning becomes an important stage of care and must be carried out within a certain time frame and according to established technology.
Interesting! We read about a beautiful flower - perennial evening primrose.
Autumn “cutting” of fruit and berry crops is carried out annually after the end of sap flow, before the first frost. Depending on the plant species, some perform the procedure in September, others in November. General recommendations are as follows:
- Pruning in autumn is carried out only in regions where there are no long and severe winter frosts. Otherwise, the bark at the cut site will freeze and the bush will die.
- The procedure is not carried out if the outside temperature is less than -10 degrees. In persistent frosts, wood acquires a fragile structure and simply breaks, causing mechanical damage that is difficult to heal.
- Freshly planted shrubs are not pruned, as this is not necessary in the first year. Moreover, if the planting site is chosen incorrectly and the plant is replanted next year, then it is best to form the crown in a new area.
- Autumn pruning applies only to mature trees and shrubs.
- Treatment of cut areas of branches with garden varnish is required.
- Tools must be sharpened as sharply as possible.
Shoots are pruned depending on the species. So, for black currants, the fruiting period lasts about 5 years, so only old branches that are 6 years old are removed.
Raspberries
If the raspberries are not remontant, the procedure is carried out immediately after harvesting. For early varieties, this may even be in the summer. Late-ripening and remontant ones are pruned only in the fall.
The life span of raspberries is 2 years. In the first year the bush actively develops, in the second it bears fruit. Subsequently, the plant begins to degenerate and gradually dies. Therefore, after harvesting for the 2nd year, it is cut off at the root. The number of shoots should also be regulated: the more there are, the smaller the harvest. Ideally, no more than 8 strong and strong shoots are left, the rest are mercilessly removed to the ground.
Remontant raspberries begin to bear fruit in the first year, so they are pruned immediately after harvest. The cut bushes are burned. If the winter in the region has little snow, pruning is carried out by weight. In winter, raspberries are tied in a bunch and bent to the ground.
Currant
Currants are pruned either during berry picking or after, when the bushes have completely shed their leaves and a dormant period begins. It bears fruit both on young shoots and on old branches. But the older the bush, the smaller and smaller the fruits. During the procedure, no more than 10 of the strongest branches and 4 young strong shoots are left on it (5 buds are cut off from the top).
Bushes over 6 years old are removed to the first true bud, which is about a third of the branch. Dried ones are cut out completely. Young shoots at the roots are carefully thinned out. Immediately after pruning, the currants are earthed up to stimulate the growth of shoots from the root system. The most powerful of them are used to replace old and diseased branches next year.
Red and white currant varieties bear fruit on mature branches. Therefore, when forming a bush, no more than 3 shoots are left each year, the rest are eliminated. As soon as berries stop appearing on the tops, they are reduced to the first fork. If fruiting does not occur the next year, the branch is removed completely.
Gooseberry
Any gooseberry varieties are prone to active growth both in width and height. Therefore, it is important to prune it annually after berry picking and leaf fall.
Dried, twisted, old branches and branches growing inside the bush must be removed at the root. If they are left, the yield will decrease every year. In autumn, 5-6 of the strongest branches are left on the gooseberry, reduced to a height of 25 cm, everything else is mercilessly removed. If time for pruning is missed and the plant is more than 2 years old, then in addition to sanitary thinning, curved branches growing down and inward are additionally cut off, fresh shoots are reduced to 3 buds. The root shoots are carefully thinned out.
Autumn diet
How should you fertilize perennial flowers and ornamental shrubs in the fall?
Experienced amateur gardener Elena Mikhailova answers :
— While we generously feed annual garden plants before harvesting, we need to be much more careful with perennial crops. It’s better not to feed anything at all than to overdo it with fertilizers. Nitrogen fertilizers are especially dangerous: they stimulate further growth and slow down the ripening of tissues, and in trees and shrubs, lignification of young shoots. Plants that fail to prepare for winter may freeze. On the contrary, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers improve the development of the root system, promote better ripening and increased winter hardiness of buds and wood, and increase plant resistance to adverse factors.
Harmful:
Complex mineral mixtures with a significant nitrogen content (for example, nitroammofoska, azofoska, etc., as well as ready-made mixtures labeled “lawn” or “spring”).
Any highly soluble and fast-acting organic fertilizers (infusion of grass, bird droppings, slurry). The best time for their use is May-June, and in August-September they are strictly contraindicated for perennial plants.
Useful:
Potassium and phosphorus fertilizers, microelement additives (in quantities specified by the manufacturer on the packaging). A good choice is potassium monophosphate: this fertilizer contains both phosphorus and potassium, is highly soluble and quickly absorbed by plants, unlike, say, superphosphate, which is long-acting. You can also use ready-made fertilizer mixtures, but only special ones for autumn application (with a nitrogen content of no more than 5–10%).
Well-rotted organic matter (peat, humus, compost) as an additive to the soil between bushes or organic mulch.
Mulch from plant waste (grass clippings, straw, fallen leaves, crushed bark or wood chips). It decomposes slowly and does not upset the nutritional balance. In addition, loose materials located on the soil surface noticeably smooth out sharp fluctuations in temperature and humidity in the area of roots and wintering buds, which helps plants more easily endure the unpredictable vagaries of autumn and winter weather. But don’t overdo it with the layer thickness: 2–4 cm is enough! The clumped, airtight “compress” that a thick layer of damp organic matter turns into during the humid fall can easily become a source of problems.
Wood ash (100–200 g per square meter). It is a source of not only potassium and phosphorus, but also calcium, magnesium and many other trace elements.
Formation of a dwarf apple tree
You can and should prune an apple tree. But they do it differently, depending on the desired end result and age.
The best time for the first pruning is autumn planting of an apple tree. During this period, the future crown is formed. The branches are cut by a third of the length at the top and a quarter at the bottom. They are removed according to the principle: the smaller the root system, the more they should be pruned.
In the second season, the apple tree is pruned 35 cm (necessarily above the bud) from the trunk of the first order branches. Subsequently, branches of the second order are formed here. But it is important to ensure that they are located strictly along the outer edge of the crown and do not bend at an acute angle. If this happens, they are shortened by 25 cm from the trunk.
It is important to remember that the fruiting age is 4 years. In this regard, all older branches are removed, replacing them with young annual shoots.
During fruiting and harvesting, it is necessary to prune emerging shoots on skeletal branches if they grow more than 20 cm. Pruning is done to approximately ¼ of the length. As a result, the tree will not be depleted, the apple harvest will become uniform, abundant and annual.
Rejuvenation is carried out after about 5 years, when the quantity and quality (size) of the fruit decreases significantly, shoots appear rarely, and they are very weakened. Pruning in this case consists of removing branches that have formed over 3 years. All branches of the first order must be replaced by branches of the second. All the strongest and fattest are also subject to elimination. As a result, the crown volume will increase. The yield may decrease, but the fruits will become noticeably larger and of better quality.
How to properly prune fruit trees in the fall
The desire of gardeners to increase the fruitfulness of fruit trees is understandable. To make fruit pruning correct and effective, you need to do it according to the following rules:
- we leave only the branches growing parallel to the soil; they contain the most fruits;
- do not remove skeletal branches that grow in the wrong direction. You will have to wait several years for the harvest, so you will have to stretch them, bending them to the ground. An abnormally growing skeletal branch is carefully bent down and secured with a rope and a peg. After 2-3 weeks, the branch is pulled back a little more. In the fall, the branch will no longer need tying;
- we remove the tops, everything broken and growing inside the crown;
- if there are two branches nearby that obviously interfere with each other’s growth, then we remove the weaker one;
- we remove branches that grow at an acute angle to the supporting branch;
- We treat all places of cuts and cuts with garden varnish. In its absence, you can use natural-based oil paint. Otherwise, the tree will begin to bleed sap, and the open wound is ready to receive infections;
- Don’t forget to remove all the trimmings and burn them.
Bud and ring cutting technology
The ring cutting technology is carried out when it is necessary to remove a branch with a wide base. It could be a weak or broken branch. Consider the base of the branch: it resembles a ring. This part is capable of actively healing the wound at the cellular level.
Pruning is carried out along the edge of the ring bead. First, a large branch must be removed by sawing it off near the ring. First, it is important to cut 1/3 of the bottom with a hacksaw - this will prevent breakage and damage to the bark. Then they saw from above. After this, all that remains is to remove the stump - work begins along the upper edge of the ring.
The cut should be smooth; if necessary, clean it with a sharp knife.
The saw cuts need to be treated with brilliant green or a special biological preparation called Farmiod and covered with garden varnish or paint. Stumps cannot be left, nor, indeed, can the branch be removed along with the ring influx: such actions lead to the formation of hollows, cracking, rotting and drying out. Many pests and fungi will be delighted by such incorrect actions.
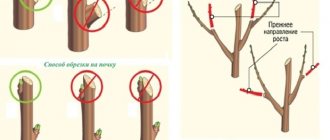
What to do if everything is carefully examined, but the annular influx is not noticeable? Move the tool slightly away from the base of the branch by 2-3 cm and make a slightly oblique cut. There is external and internal pruning “to the bud” and the meaning of both procedures is to shorten the shoots to stimulate branching of the crown. Especially effective for shrubs. How to figure out which method is needed in your case: thickening in, excessive spreading - “inner bud”. With the first method, the shoot must be shortened to the outer bud, looking from the center, and with the second, it is shortened to the bud, looking inside the crown.
An example of shortening “to the outer bud”
In both options, the cut is made obliquely, not exceeding 0.5 cm from the kidney. Tall stumps are difficult to heal, and a low cut can affect the bud.
Instructions for pruning young fruit trees
| Illustration | Description of action |
| Let's give a clear example of pruning. Here is a heavily thickened crown of a young fruit tree. We will need a hacksaw and pruning shears. We start with a careful examination and determine what kind of circumcision is necessary. | |
| First, we remove the tops in the center of the crown; they will still be of no use. | |
| We remove stumps, if any. | |
| We shorten thin branches by several buds. | |
| Using pruning shears we cut off the branches growing inside the crown. | |
| We cut down particularly thick stumps with a hacksaw from below. | |
| We remove the branches that form an acute degree with the skeletal ones. | |
| Once again, please note that the cut is made from below, stepping back a couple of cm from the base. | |
| There should be a smooth, neat cut left. | |
| We shorten the thinnest branches by several buds. | |
| Excess skeletal branches that interfere with others need to be cut down into a ring. | |
| First, they make a cut from the bottom, since the branch is thick, they finish it from the top. | |
| This is what a thinned crown looks like when it is properly formed. |
Mandatory feeding after the procedure
Pruning is always a traumatic procedure for shrubs. Therefore, the next step will be the application of organic fertilizers. Spring feeding differs significantly from autumn feeding.
If the pruning procedure was carried out from August to November, then the plant will need phosphorus fertilizers to form a new root system. When applying fertilizing, it should be evenly redistributed around the entire circumference around the stem circle. This process is combined with watering.
You will be interested to read about an unusual bush - David's Buddleia.
The most effective organic fertilizer for shrubs is compost infusion. It is prepared for about 3 days in the proportion of 0.5 kg per 10 liters of water. Watering is carried out in the evening when it is not hot or in cloudy weather. When applying fertilizer, make sure that the liquid does not get on young shoots and leaves. If the drought lasts for a long time, the plant is watered abundantly with plain water before fertilizing.
Pruning ornamental and fruit crops is not very difficult. The main thing is to choose the right time, stock up on tools and be patient at first. In the future, when the necessary skills are acquired, this process will be simplified, and every year the plot will delight with a lush, healthy, flowering and fruit-bearing garden.